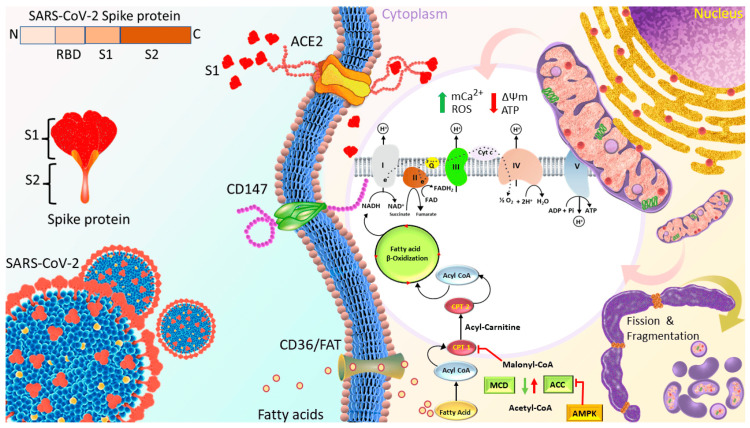
Figure 1. Proposed Mechanisms Through Which S1 of Spike Protein Induced Cardiac Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Which Leads to Cardiac Injury in COVID-19 Patients.
Spike protein is the glycosylated protein that covers the surface of SARS-CoV-2 and binds to the host ACE2 receptor to mediate the viral cell entry. It is composed of S1 and S2 subunits that are responsible for ACE2 binding and membrane fusion, respectively. S1 possibly binds to ACE2 on the AC16 membrane and is then internalized into the cytosol and localized in organelles, such as mitochondria, which induces the transient increase in fatty acids transport and uptake for biogenetics, Δψm, and permanent mCa2+, and disrupts Δψm later, finally impairing mitochondrial function and promoting ROS production. In turn, ROS further exacerbates mitochondrial function and mitochondrial fragmentation. Moreover, S1 causes downregulation of TOM20; this effect might inhibit the pathways leading to mitochondrial biogenesis.
Abbreviations: ACE2 = angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, FAT = fatty acid translocase, PCT1/2 = Carnitine palmitoyltransferase ½, MCD = Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase, ACC = acetyl-CoA carboxylase, AMPK = AMP-activated protein kinase, mCa2+ = mitochondrial calcium, Δψm = mitochondrial membrane potential, ROS = reactive oxygen species.
*Figure and legend reprinted from Huynh et al. [14]. The legend title has been slightly adapted. Permission to use this figure has been granted in accordance with the open access Creative Common CC BY 4.0 license.