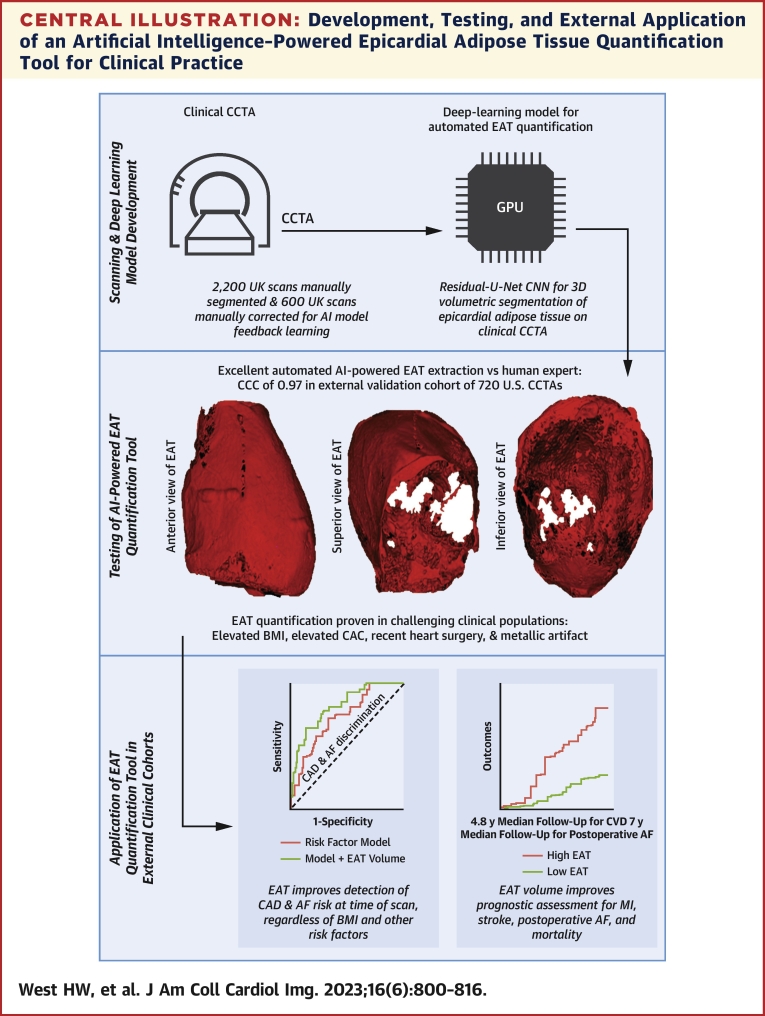
Central Illustration.
Development, Testing, and External Application of an Artificial Intelligence–Powered Epicardial Adipose Tissue Quantification Tool for Clinical Practice
(Top) A deep-learning model was trained to automatically extract the adipose tissue from CCTA. (Middle) The model performed excellently compared to human segmentation in internal and external testing, including in patient groups that are commonly occurring yet challenging for CCTA. (Bottom) The final automated artificial intelligence (AI) model for epicardial adipose tissue (EAT) quantification was applied to external clinical cohorts and revealed improved detection of prevalent disease risk for coronary artery disease (CAD) and atrial fibrillation (AF) and provided incremental prognostic benefit for key cardiovascular events such as myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, postoperative AF, and mortality in longitudinal cohorts. 3D = 3-dimensional; BMI = body mass index; CAC = coronary artery calcium; CCC = Lin concordance correlation coefficient; CNN = convolutional neural network; CCTA = coronary computed tomography angiography; CVD = cardiovascular disease; GPU = graphics processing unit.