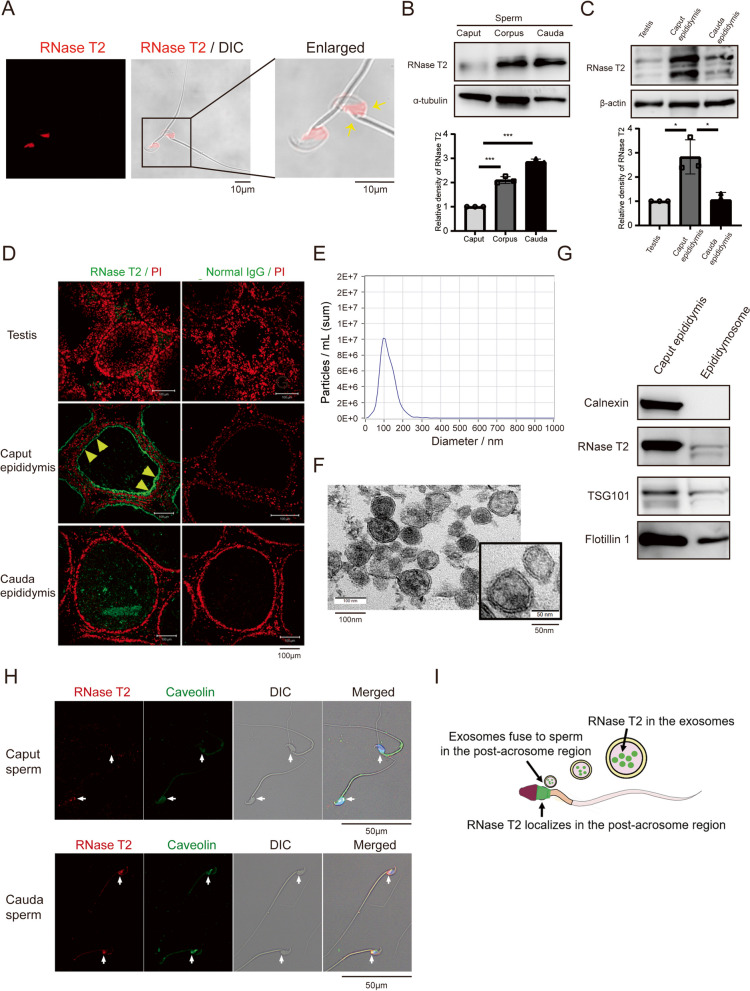
Fig. 1.
RNase T2 in caput epididymis can be transferred to spermatozoa through release of exosomes into the seminal plasma. A Immunofluorescent staining of RNase T2 (red fluorescence) in mature spermatozoa. Yellow arrow indicates RNase T2 staining in the post-acrosomal region of spermatozoa. Differential interference contrast (DIC) images showed the sperm shape. Scale bar, 10 μm. B Western blot detection of RNase T2 protein in caput sperm, corpus sperm, and cauda sperm respectively. Quantification of Western blots, normalized to α-tubulin (n = 3). C, D Western blot detection (C) and immunofluorescence staining (D) of RNase T2 in the testis, caput epididymis, and cauda epididymis indicated its high abundance in the caput epididymis. Quantification of Western blots, normalized to β-actin (C, n = 3). Scale bar, 100 μm. E Nanoparticle tracking analysis of the isolated epididymal-derived exosomes showed that their diameters vary from 50 to 150 nm. F TEM analysis showed the size and the lipid bilayer structure of the isolated epididymal-derived exosomes. Scale bar, 10 nm. G Western blot analysis of exosome markers and RNase T2 in isolated epididymal-derived exosomes. H Immunofluorescence staining of RNase T2 (red) and Caveolin 1 (green) in mouse sperm. DIC images showed the sperm shape. Scale bar, 50 μm. I Schematic of RNase T2 in caput epididymis transference to spermatozoa through exosomes. Data are expressed as means ± SD; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001