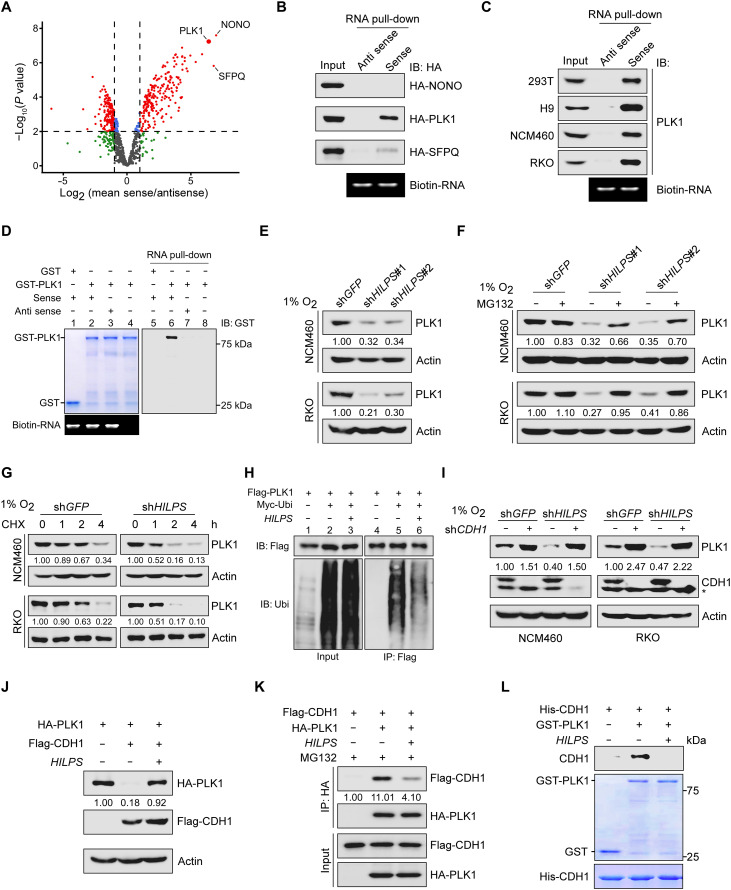
Fig. 4. HILPS binds to PLK1 and enhances PLK1 stability.
(A) Volcano plots showing HILPS interacting proteins pulled down from 293T cells exposed to 1% O2 using biotin-labeled HILPS. Proteins significantly enriched (fold change > 2 and P < 0.01) from three independent experiments are displayed as red dots. (B) Biotin-labeled HILPS pull-down assay using 293T cell lysates with respective hemagglutinin (HA)–tagged protein expression. IB, immunoblot. (C) Biotin-labeled HILPS pull-down assay to detect endogenous PLK1 in 1% O2-treated cells. (D) In vitro RNA pull-down assay using biotin-labeled HILPS and recombinant GST-PLK1. (E) Immunoblots of PLK1 in HILPS-depleted NCM460 and RKO cells exposed to 1% O2. (F) Immunoblots of PLK1 in HILPS-depleted NCM460 and RKO cells treated with MG132 (10 μM) for 6 hours before harvest. (G) Time-course analysis of PLK1 degradation. HILPS-depleted NCM460 and RKO cells were cultured in 1% O2, treated with cycloheximide (CHX; 100 μg/ml) and harvested at the indicated time points, followed by immunoblotting of PLK1. (H) Analysis of PLK1 polyubiquitination in the presence or absence of HILPS in 293T cells. (I) Immunoblots of PLK1 and CDH1 in 1% O2-cultured NCM460 and RKO cells expressing shRNA targeting HILPS and/or CDH1. Asterisk denotes a nonspecific band detected by CDH1 antibody. (J) Immunoblots of indicated proteins in 293T cells transfected with HA-PLK1, Flag-CDH1, and/or HILPS. (K) Co-IP to detect protein interaction between PLK1 and CDH1 in the absence or presence of HILPS. 293T cells were treated with MG132 (10 μM) for 6 hours before harvest. (L) In vitro protein binding assay to detect PLK1-CDH1 interaction in the absence or presence of in vitro transcribed HILPS.