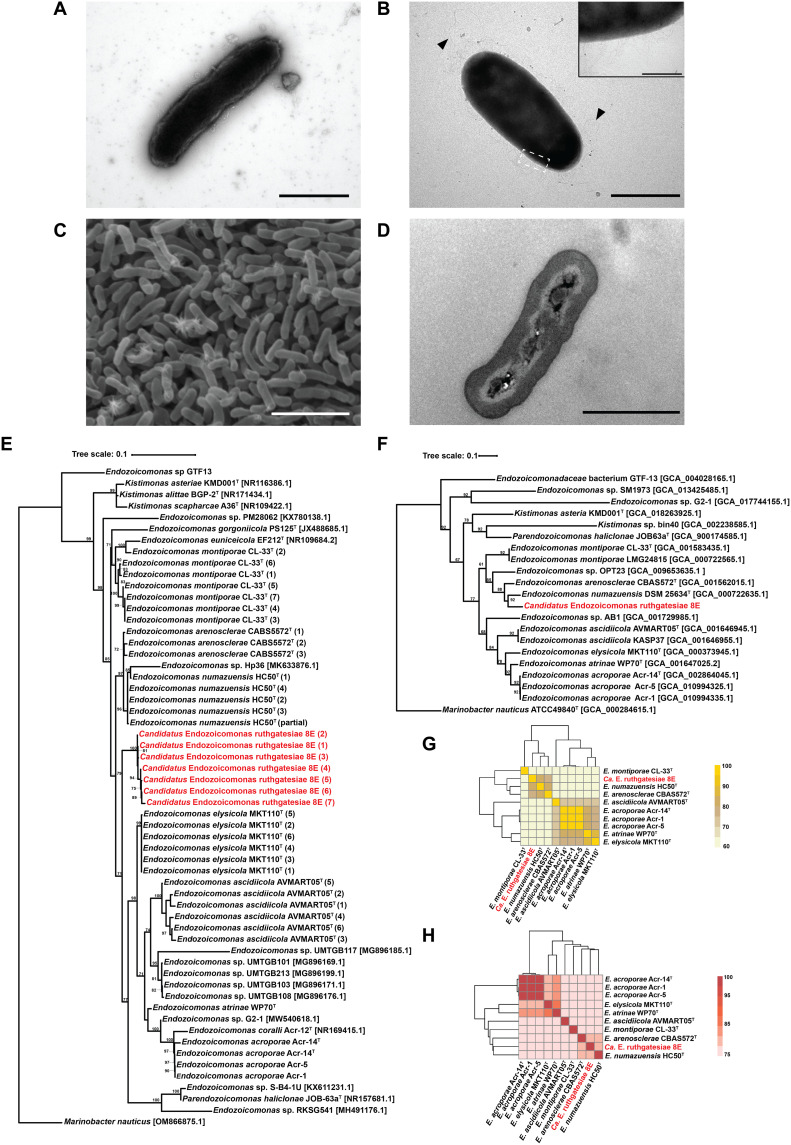
Fig. 1. Morphological and taxonomic characteristics of the genus Endozoicomonas.
(A) Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) image. Bacteria were incubated in mmbv4 medium. Negative stained by 2% phosphotungstic acid. Scale bar, 1 μm. (B) TEM image. Bacteria were incubated in minimal medium with 0.1 mM DMSP. Scale bar, 1 μm. Triangles indicate the peritrichous flagella-like structures, and the insert is the magnification (×10) of fimbriae-like structure. Insert bar = 0.1 μm. Negative stained by 2% uranyl acetate. (C) Bacterial colony surface observed by SEM. Scale bar, 10 μm. (D) Bacterial TEM thin section. Scale bar, 1 μm. (E) The maximum likelihood tree was calculated with MEGA11.09 and tested by bootstrap method with 1000 replications using the Tamura 3-parameter model. The bootstrap values are shown at the corners of branching points. Bacteria used for the analysis in this study are noted with GenBank accession numbers, and the asterisk “*” indicates that the 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) sequence was annotated by Prokka 1.14.6. For each strain, only one copy of 16S rRNA underwent analysis. (F) Phylogenetic tree built by up-to-date bacterial core gene sets (concatenated alignment of 92 core genes). The phylogenetic tree is based on whole genome sequences, and RAxML (Randomized Axelerated Maximum Likelihood) was used for phylogeny reconstruction. The length of concatenated alignments was 84741, the GenBank accession numbers are shown in parentheses, and gene support indices are given at the corner of branching points. (G) Average nucleotide identity (ANI). (H) Average amino acid identity (AAI).