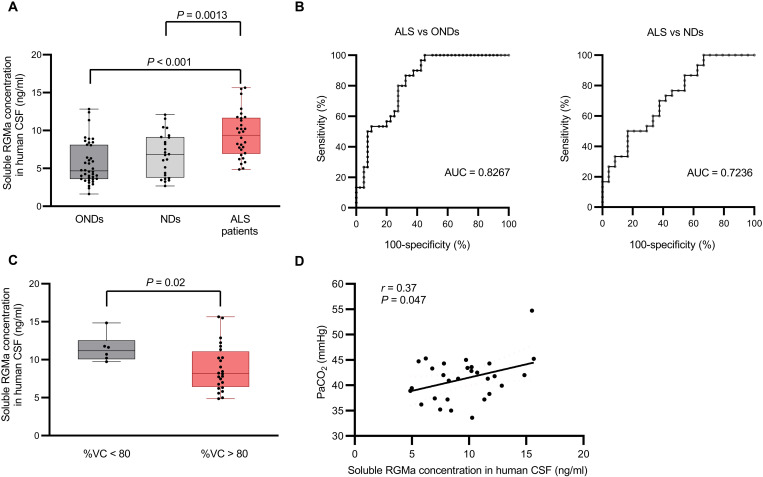
Fig. 1. RGMa was significantly elevated in the CSF of patients with ALS.
(A) RGMa in the CSF of patients with neurological disorders and control patients was measured using ELISA. RGMa was significantly increased in patients with ALS (n = 30) compared to those with NDs (n = 24) and ONDs (n = 40). (B) ROC analysis revealed that an AUC was high enough to distinguish ALS from NDs and ONDs. (C) The RGMa levels in the CSF were higher in patients with ALS with less than 80%VC than in those with more than 80%. (D) RGMa levels in the CSF were correlated with PaCO2 in patients with ALS. Error bars indicate mean ± SEM. RGMa, repulsive guidance molecule A; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; ALS, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; NDs, nonneurodegenerative disorders; ONDs, other neurodegenerative disorders; ROC, receiver operating characteristic; AUC, area under the curve; PaCO2, partial pressure of CO2 in arterial blood; %VC, vital capacity percentage.