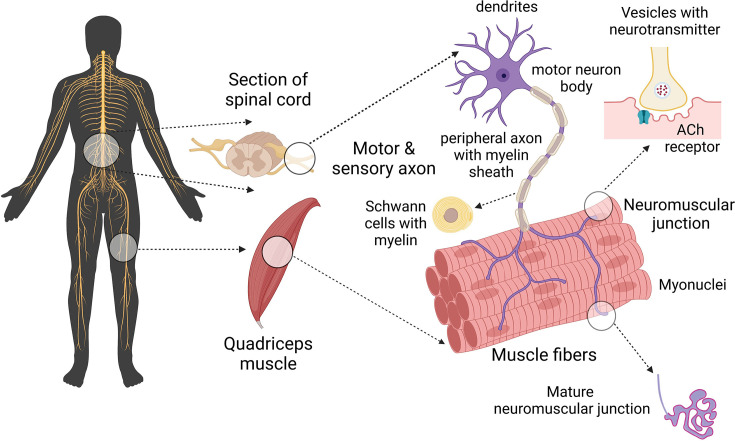
Figure 4. Key components of motor unit and neuromuscular junction.
Schematic diagram of the motorneuron-skeletal muscle connection that is critical for the transfer of electrical signals for myofibre contraction. The motorneuron cell body in the spinal cord, sends an electrical signal down the motorneuron axon to the NMJ on the surface of an individual myofibre. The pre-synaptic nerve terminal release vesicles containing the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, this binds to receptors on the post-synaptic folds on the myofibre surface (sarcolemma). This signal is transferred along the myofibre surface and then into the T-tubules to initiate contraction. In mature human NMJs, the post-synaptic junction on each myofibre forms complex folds, a typical form of mature NMJ (in red; bottom right). The NMJ is innervated by a single motor axon (in purple; bottom right). Created with BioRender.com.
ACh receptor, acetylcholine receptor.