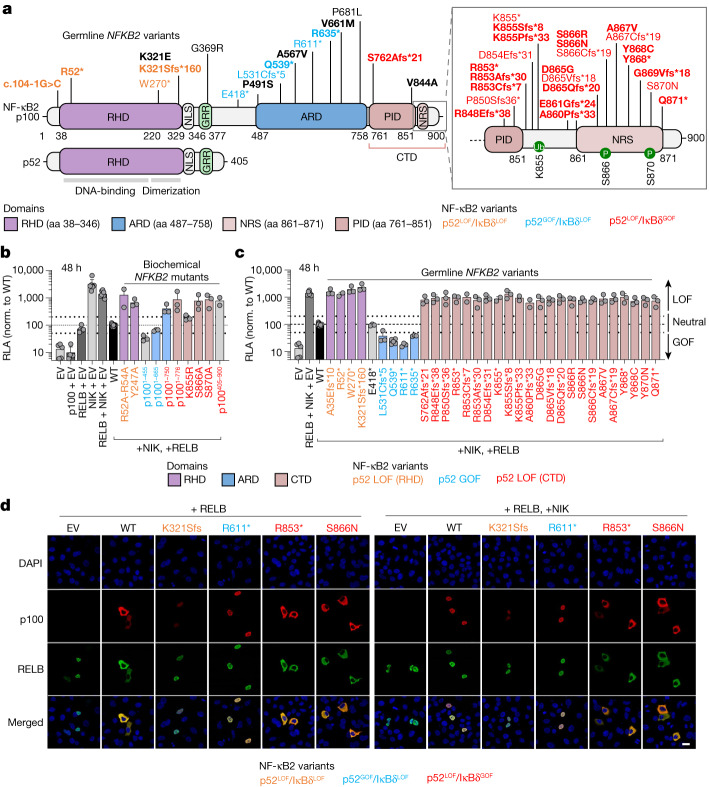
Fig. 1. Functional testing of the NFKB2 alleles by overexpression.
a, Schematic of the NF-κB2 protein (p100 and p52) with the variants, identified in heterozygous patients, that were included in this study (n = 28 variants, shown in bold) or not included here but reported elsewhere (n = 13 variants). The C-terminal domain (CTD) spans amino acids (aa) 760–900. The REL-homology domain (RHD; purple), the ankyrin repeat domain (ARD; blue) and the CTD, including the processing-inhibitory domain (PID) and the NIK-responsive sequence (NRS) (brown), are shown. The NFKB2 variants that are LOF for p52/p52 repression of κB transcriptional activity (p52 activity) and LOF for IκBδ regulatory activity (p52LOF/IκBδLOF) are shown in orange. The variants that are GOF for p52 activity and LOF for IκBδ activity are shown in blue (p52GOF/IκBδLOF). The variants in the CTD that are both LOF for the p52 activity and GOF for the IκBδ regulatory activity (p52LOF/IκBδGOF) are shown in red. Neutral NFKB2 variants are shown in black. b, The relative luciferase activity (RLA) of HEK293T cells transfected with a κB reporter luciferase construct (κB-luc) in the presence or absence of plasmids encoding NIK, RELB and/or p100/NF-κB2 WT or biochemical p100/NF-κB2 mutants reported in previous studies, normalized (norm.) to WT p100/NF-κB2, after 48 h of transfection. Data are mean ± s.d. from three independent experiments. EV, empty vector. c, The RLA of HEK293T cells transfected with a κB-luc vector, in the presence of plasmids encoding NIK, RELB and p100/NF-κB2 WT or the NFKB2 variants included in this study or reported in previous studies, at 48 h after transfection. Data are mean ± s.d. from three independent experiments. d, Subcellular localization of the WT or the NF-κB2 variants used for cotransfection with RELB without (left) or with (right) NIK, as determined by confocal microscopy analysis of HeLa cells. The nuclei were stained with DAPI; p100 and RELB were detected using antibodies recognizing their N-terminal domains. Data shown are representative of two independent experiments. Scale bar, 20 μm.