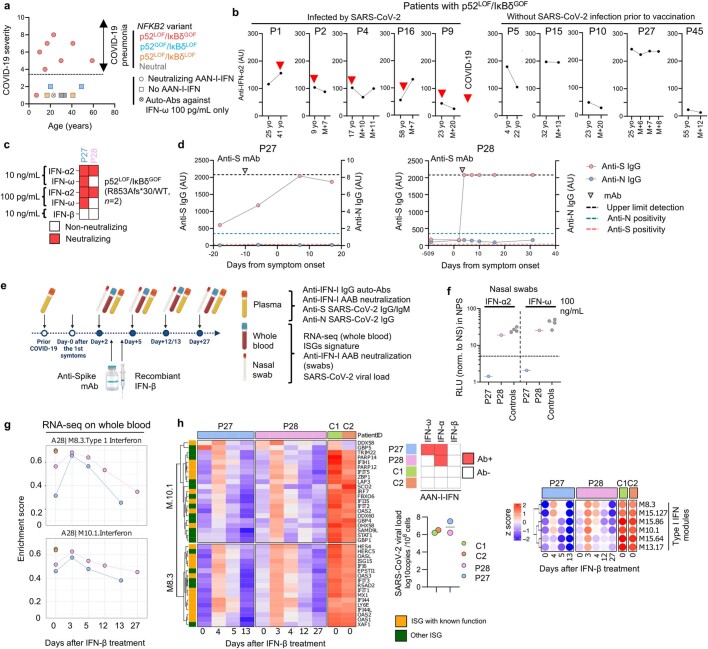
Extended Data Fig. 9. AAN-I-IFNs prevent ISG induction in blood and the upper respiratory tract during COVID-19, a defect that can be rescued by exogenous IFN-β treatment.
(a) Correlation between age and COVID-19 severity in patients with inborn errors of NF-κB2. The crossed light red square represents a patient with auto-Abs neutralizing only IFN-ω at 100 pg/mL. (b) Changes in the titres of auto-Abs against IFN-α2, as measured by Gyros, with age, in patients with a p52LOF/IκBδGOF variant and COVID-19. Red arrows indicate the onset of COVID-19. (c) Heatmap showing the neutralization profile of P27 et P28 heterozygous for a p52LOF/IκBδGOF variant (R853Afs*30/WT) during COVID-19. (d) Longitudinal follow-up of anti-S and anti-N IgG in P27 and P28 during the course of COVID-19, before and after treatment by the infusion of an anti-S monoclonal Ab (mAb, grey arrow). (e) Overview of the longitudinal investigation of COVID-19 episodes in P27 et P28. (f) Neutralization capacity of the nasal swab from P27 et P28 upon SARS-CoV-2 infection and individuals infected with the omicron variant but without detectable AAN-I-IFNs (controls, n = 4, grey dots). Bars represent the median. (g) Longitudinal IFN module enrichment score during the course of COVID-19 in P27 and P28 and in two age-matched controls infected with SARS-CoV-2. IFN modules M.10.1 and M.8.3 are represented. Values obtained before and after the treatment of P27 and P28 with IFN-β. (h) ISG score induction by IFN module analysis during the course of COVID-19 in P27 and P28, before and after recombinant IFN-β treatment, and in age-matched controls (C1 and C2, n = 2) infected with SARS-CoV-2.