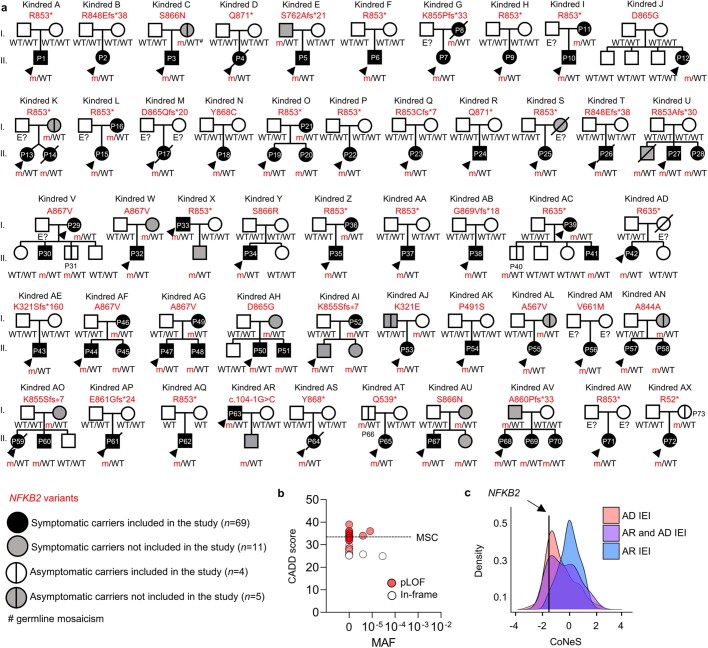
Extended Data Fig. 1. Pedigrees of the 73 patients studied carrying heterozygous NFKB2 variants.
(a) Pedigrees of the patients heterozygous for rare variants of NFKB2. Generations are indicated by Roman numerals (I–II), and each symptomatic carrier included in the study, represented by a black symbol, is indicated as P followed by an Arabic numeral (P1–P73). Grey symbols represent relatives who are symptomatic carriers but for whom no material was available for this study. A vertical bar, within a white or grey symbol, indicates an asymptomatic carrier included or not included (due to a lack of available material), respectively in the study; an arrow indicates the index case; a black diagonal line indicates that the individual is deceased. “E?” indicates individuals of unknown genotype. (b) CADD-MAF (combined annotation-dependent depletion-minor allele frequency) graph of the rare or private NFKB2 variants (n = 28) from the 73 patients recruited. The red and white dots represent pLOF and missense heterozygous NFKB2 variants, respectively. Each score was calculated with CADD version 1.6. The dashed line represents the mutation significance (MSC) cutoff threshold of 33 for NFKB2. (C) CoNeS score of the NFKB2 gene.