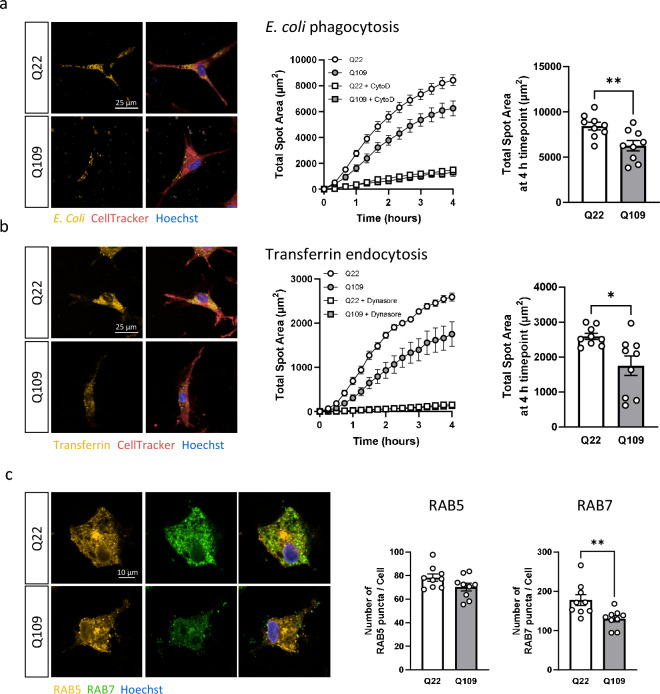
Figure 3.
Q109 iPSC-microglia showed impairment in phagocytosis and endocytosis. (a) Phagocytosis was assessed via the uptake of pHrodo-conjugated E. coli particles. Q109 and Q22 iPSC-microglia were imaged every 20 min for 4 h. Uptake of E. coli particles was inhibited by the addition of 30 μM cytochalasin D (CytoD) for 1 h prior and during phagocytosis. Total spot area of phagocytosed E. coli after 4 h was significantly reduced in Q109 iPSC-microglia compared to Q22 control iPSC-microglia. (b) Endocytosis was assessed via the uptake of pHrodo-conjugated transferrin particles. Q109 and Q22 iPSC-microglia were imaged every 15 min for 4 h. Uptake of transferrin particles was inhibited by the addition of 30 μM dynasore for 1 h prior and during endocytosis. Total spot area of transferrin particles was significantly reduced in Q109 iPSC-microglia compared to Q22 control iPSC-microglia. (c) Early and late endosomes were identified by immunostaining using the early endosome marker RAB5 and late endosome marker RAB7. Number of RAB7, but not RAB5 puncta/cell were significantly decreased in Q109 iPSC-microglia cells. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. n = 3 independent experimental repeats with 3 clones. Statistical analysis was performed using unpaired t-test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.