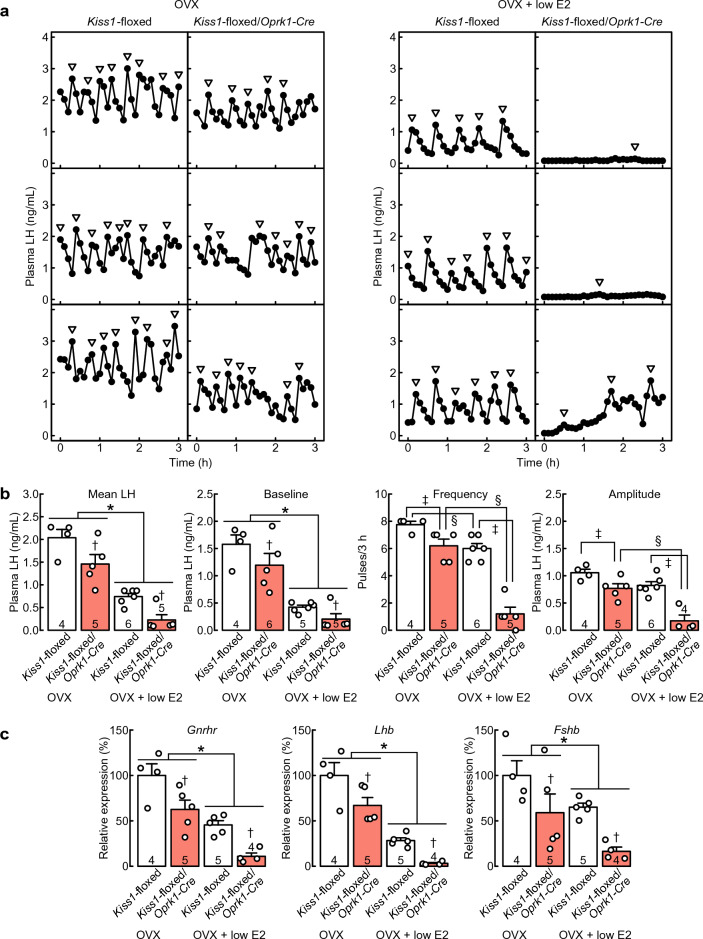
Figure 4.
OVX Kiss1-floxed/Oprk1-Cre rats, whose Kiss1 was deleted in kisspeptin neurons expressing or having expressed Oprk1, without E2 treatment showed frequent luteinizing hormone (LH) pulses, whereas OVX + low E2 Kiss1-floxed/Oprk1-Cre rats exhibited profound disruption of LH pulses. (a) Plasma LH profiles in three representative animals from the OVX or OVX + low E2 Kiss1-floxed/Oprk1-Cre group and Cre(−)/Kiss1-floxed control group. Arrowheads indicate LH pulses identified with the PULSAR computer program. (b) Mean LH concentrations and the baseline, frequency, and amplitude of LH pulses in OVX or OVX + low E2 Kiss1-floxed/Oprk1-Cre rats and Cre(−)/Kiss1-floxed control rats. (c) Pituitary Gnrhr, Lhb, and Fshb mRNA expression in OVX or OVX + low E2 Kiss1-floxed/Oprk1-Cre rats and Cre(−)/Kiss1-floxed control rats were determined by reverse transcription-quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR). Open circles indicate the individual data. Values are the means ± SEM. Numbers in (or on) each column indicate the number of animals used. Asterisks indicate statistically significant main effects of E2 treatment (p < 0.05) based on two-way ANOVA. Daggers indicate statistically significant main effects of the genotype (p < 0.05) based on two-way ANOVA. Double daggers indicate statistically significant differences between Kiss1-floxed/Oprk1-Cre and Cre(−)/Kiss1-floxed rats within the OVX or OVX + low E2 groups (p < 0.05, the simple main effect of two-way ANOVA). Section signs indicate statistically significant differences between OVX and OVX + low E2 rats within the Kiss1-floxed/Oprk1-Cre or Cre(−)/Kiss1-floxed groups (p < 0.05, the simple main effect of two-way ANOVA).