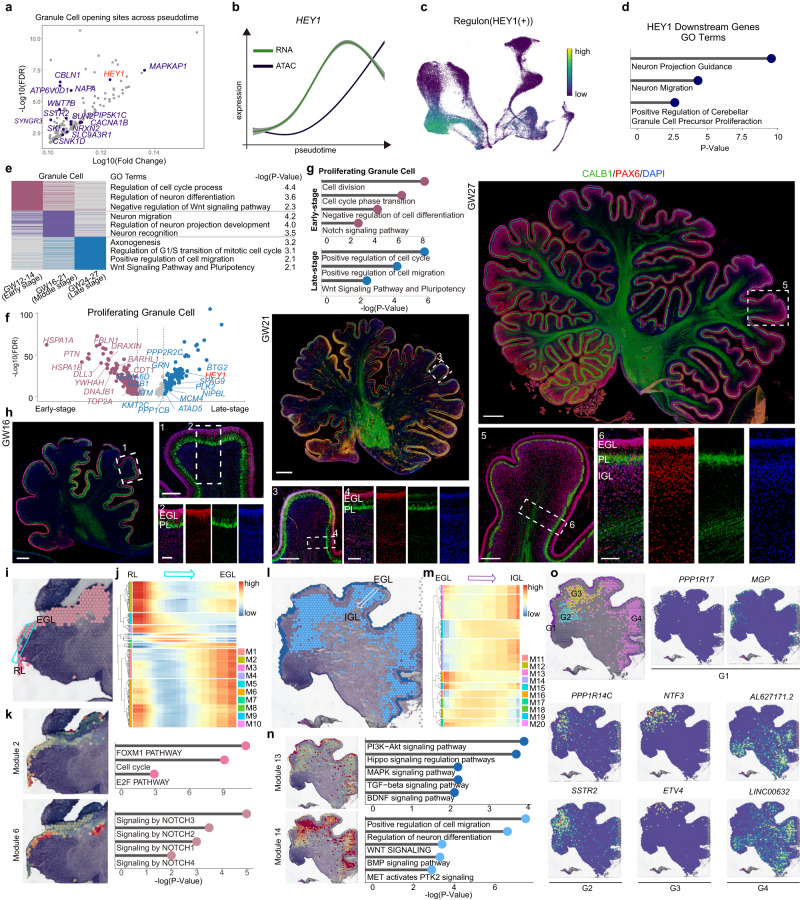
Fig. 4. Dynamics of neurogenesis of granule cells in the developing human cerebellum.
a Scatter plots depicting highly expressed peaks annotated by mapping to the hg19 human genome in granule cells. b Gene expression of RNA (green) and ATAC (black) across pseudotime for HEY1, the shadow represents the 95% confidence interval around the fitted curve. c Regulon HEY1 patterns shown in the UMAP plots using the same layout as Fig. 1b (RNA), black, no expression; yellow, relative expression. d GO terms of the target genes of regulon HEY1. Hypergeometric test. e Heatmap showing the differences in developing stages of granule cells. Gene ontology analysis showing the biological functions of different stages of granule cells (right). Hypergeometric test. f, g Scatter plots (f) and gene ontology (g) analysis showing the differentially expressed genes between early- (red plot) and late-stage (blue plot) proliferating granule cells. Hypergeometric test. h Immunofluorescence images of CALB1 and PAX6 in GW16, GW21 and GW27. Scale bar, GW16, 500 μm (left), 200 μm (right, top), 100 μm (right, bottom); GW21, 1000 μm (top), 300 μm (left, bottom), 100 μm (right, bottom). GW27, 1000 μm (top), 300 μm (left, bottom), 100 μm (right, bottom). The experiments were repeated three times independently with similar results. i–k Spatial-specific gene modules showing the gene patterns from the RL to EGL differentiation process (i, j). Modules 2 and 6 are related to the RL and EGL regions, respectively. GO terms showing the KEGG pathways in this process (k). Hypergeometric test. l–n Spatial-specific gene modules showing the gene patterns from the EGL to IGL differentiation process (l, m). Modules 13 and 14 were related to the EGL and IGL regions, respectively. GO terms showing the KEGG pathways in this process (n). Hypergeometric test. o 10x Genomics Visium data showing the spatial distribution of four subclusters of granule cells and the expression of different markers in the GW17 cerebellum.