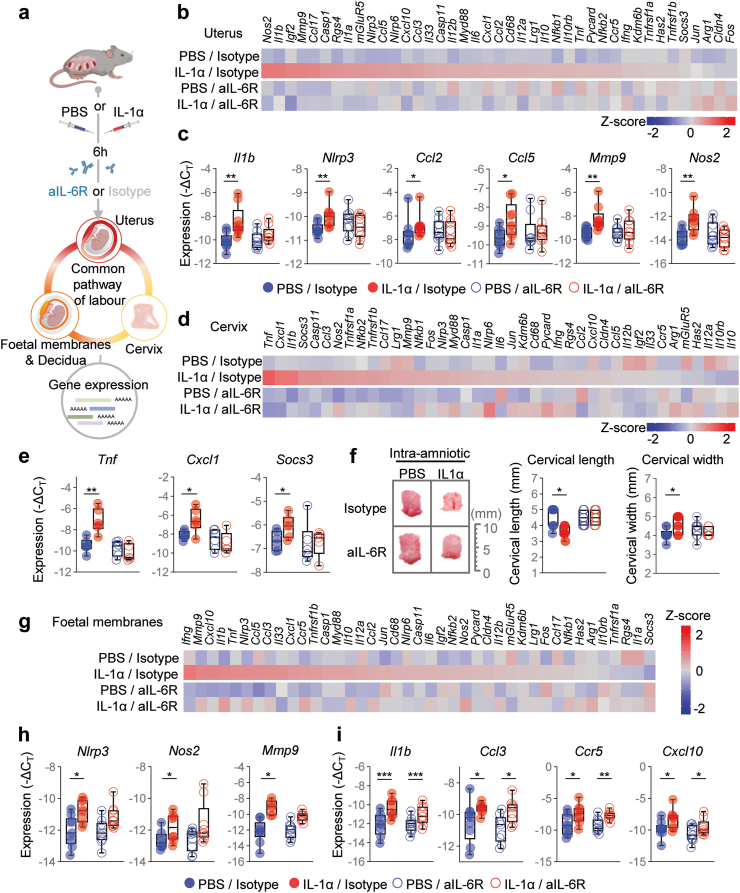
Fig. 3.
Blockade of IL-6R interferes with the common pathway of labour induced by intra-amniotic IL-1α. (a) Dams underwent intra-amniotic injection of PBS (control) or IL-1α on 16.5 days post coitum (dpc). Six h later, dams were intra-peritoneally injected with rat anti-mouse IL-6 receptor monoclonal antibody (aIL-6R) or rat IgG2b isotype (control). Sixteen h after the intra-amniotic injection, the uterus, cervix, foetal membranes, and decidua were collected to analyse gene expression by directed high-throughput RT-qPCR. (b) Heatmap representation of inflammatory gene expression in the uterine tissue (n = 9 per group). Red indicates increased expression and blue indicates decreased expression. (c) Gene expression (−ΔCT) of Il1b, Nlrp3, Ccl2, Ccl5, Mmp9, and Nos2 in the uterus. (d) Heatmap representation of inflammatory gene expression in the cervix (n = 9 per group). (e) Gene expression (−ΔCT) of Tnf, Cxcl1, and Socs3 in the cervix. (f) Representative images of cervical dilation and quantifications of cervical length and width. Scale bar represents 10 mm (n = 7–11 per group). (g) Heatmap representation of inflammatory gene expression in foetal membranes (n = 9 per group). Gene expression (-ΔCT) of (h)Nlrp3, Nos2, and Mmp9 or (i)Il1b, Ccl3, Ccr5, and Cxcl10 in foetal membranes. Data for gene expression are shown as box-and-whisker plots where midlines indicate medians, boxes indicate interquartile ranges, and whiskers indicate minimum and maximum values. p-values were determined by two-sided Mann–Whitney U-test. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001.