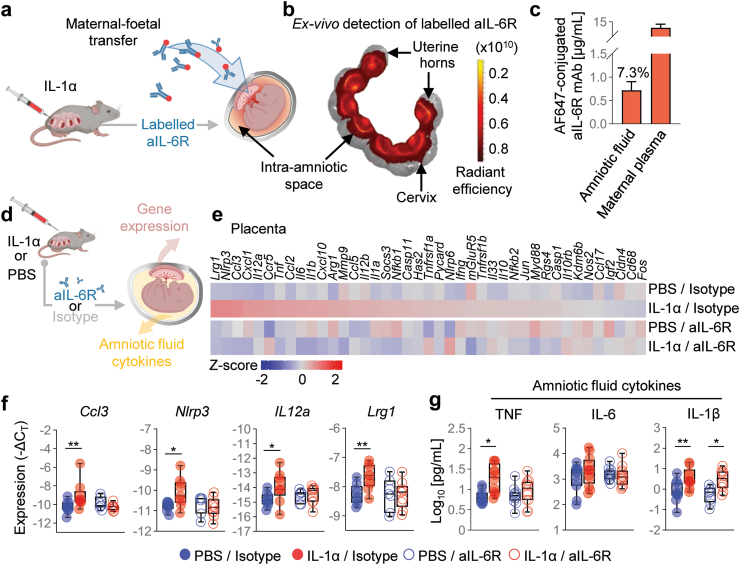
Fig. 4.
Anti-IL-6R efficiently crosses the placenta and reduces the inflammation-related gene expression induced by intra-amniotic IL-1α. (a) Dams underwent intra-amniotic injection of IL-1α on 16.5 days post coitum (dpc). Six h later, dams received Alexa Fluor™647-conjugated rat anti-mouse IL-6 receptor monoclonal antibody (aIL-6R) to evaluate maternal–foetal transfer. Sixteen h after intra-amniotic injection the uterus was collected for imaging by using the IVIS system. (b) Representative fluorescence image and scale showing the ex vivo detection of labelled aIL-6R in the intra-amniotic space. (c) Amniotic fluid concentrations (μg/mL) of aIL-6R in the amniotic fluid and maternal plasma. The amniotic fluid concentration is also reported as a percentage of the maternal plasma concentration (7.3%) (n = 5). Data are shown as bar plots with mean and S.E.M. (d) Dams underwent intra-amniotic injection of PBS (control) or IL-1α on 16.5 days post coitum (dpc). Six h later, dams were treated with aIL-6R or rat IgG2b isotype (control). Sixteen h after intra-amniotic injection, placental tissues and amniotic fluid were collected to determine gene expression and cytokine concentrations, respectively. (e) Representative heatmap showing Z-scores (red and blue indicates increased and decreased expression, respectively) for gene expression across the placental tissues from the four experimental groups (n = 7–9 per group). (f) Expression (-ΔCT) of Ccl3, Nlrp3, Il12a, and Lrg1 in the placental tissues from the four experimental groups. (g) Concentrations (pg/mL) of TNF, IL-6, and IL-1β in the amniotic fluid from the four experimental groups (n = 8–12 per group). Data for gene expression are shown as box-and-whisker plots where midlines indicate medians, boxes indicate interquartile ranges, and whiskers indicate minimum and maximum values. p-values were determined using the two-sided Mann–Whitney U-test. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01.