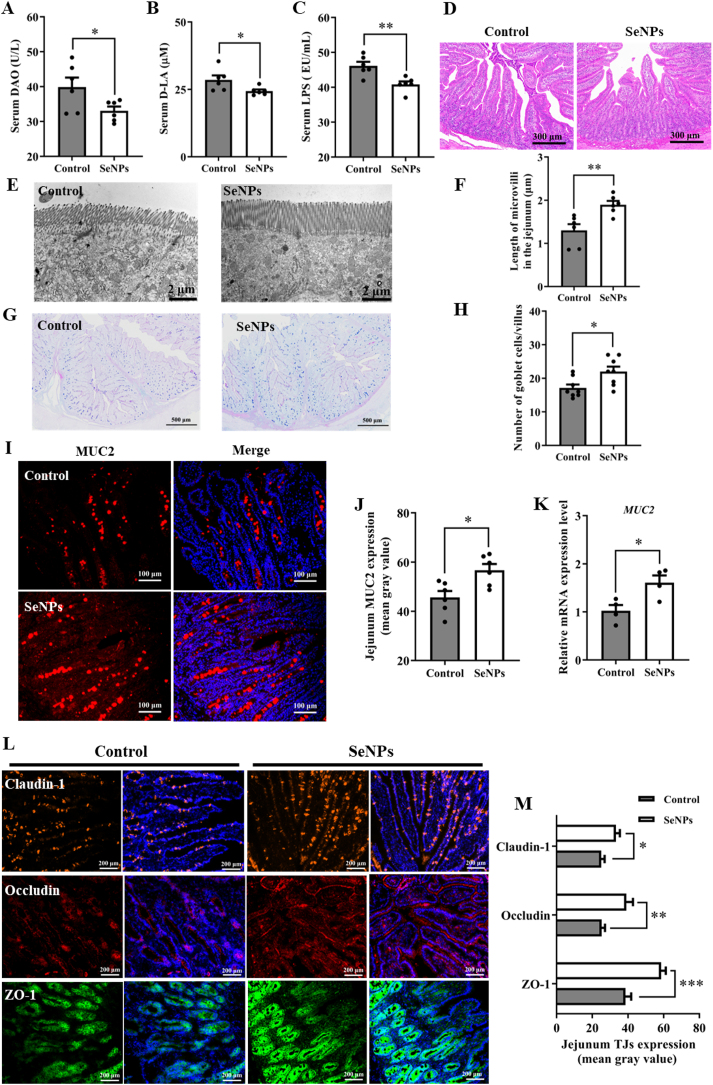
Fig. 1.
Dietary SeNPs supplementation improved intestinal barrier function of early-weaned piglets. (A) The activity of DAO in serum (n = 6). (B) The level of D-LA in serum (n = 6). (C) The level of LPS in serum (n = 6). (D) Jejunal histomorphology observed by H&E staining (n = 6). (E) TEM images of jejunal microvilli (n = 6). (F) Quantification of microvilli height in jejunum (n = 6). (G) Goblet cells in jejunum examined with AB-PAS staining (n = 6). (H) Quantification of jejunal goblet cell numbers (n = 8). (I) The expression level of MUC2 in jejunum detected by immunofluorescent staining (n = 6). (J) Quantification of MUC2 expression level in jejunum (n = 6). (K) The mRNA level of MUC2 in jejunum detected by qPCR (n = 4). (L) The expression levels of tight junction proteins (claudin-1, occludin, ZO-1) were detected by immunofluorescent staining (n = 6). (M) Quantification of the expression levels of claudin-1, occludin, and ZO-1 in jejunum (n = 6). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. ∗P < 0.05; ∗∗P < 0.01; ∗∗∗P < 0.001. SeNPs = selenium nanoparticles; DAO = diamine oxidase; D-LA = D-lactic acid; LPS = lipopolysaccharide; MUC2 = mucin 2; ZO-1 = zonula occludens-1; TJs = tight junctions.