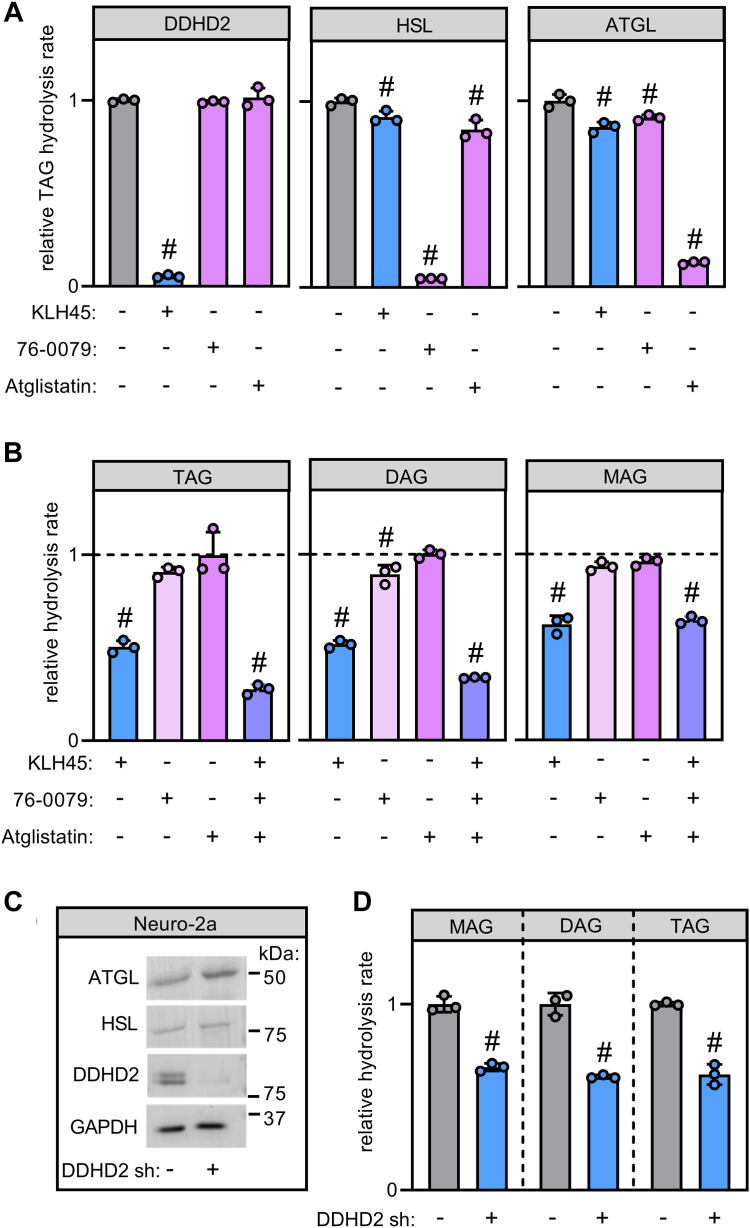
Fig. 2.
Contribution of cytosolic lipases to acylglycerol hydrolase activities of Neuro-2a cells. A: Inhibition of recombinant lipase activities by small molecules. COS-7 cell extracts expressing His6-tagged recombinant enzymes were incubated with TAG substrate in the absence or presence of Atglistatin (40 μM), 76-0079 (1 μM), or KLH45 (100 nM), and the release of fatty acids was quantified. B: Inhibition of endogenous lipase activities in Neuro-2a cells. Cellular extracts were incubated with lipid substrates and small molecule inhibitors as indicated, and the release of fatty acids was quantified. C: Western blotting analysis of lipase expression in Neuro-2a cells. Cells were transduced with lentivirus-expressing scrambled shRNA or DDHD2 shRNA, and protein expression was analyzed using specific antibodies. GAPDH was detected as a loading control. D: Lipid hydrolase activities of Neuro-2a cells after stable silencing of DDHD2 expression. Cellular extracts were incubated with lipid substrates as indicated and the release of fatty acids was quantified. Statistical significance was assessed by ANOVA (n = 3; #, P < 0.05). ATGL, adipose triglyceride lipase; DAG, diacylglycerol; DDHD2, DDHD domain-containing 2; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; HSL, hormone-sensitive lipase; MAG, monoacylglycerol; TAG, triacylglycerol.