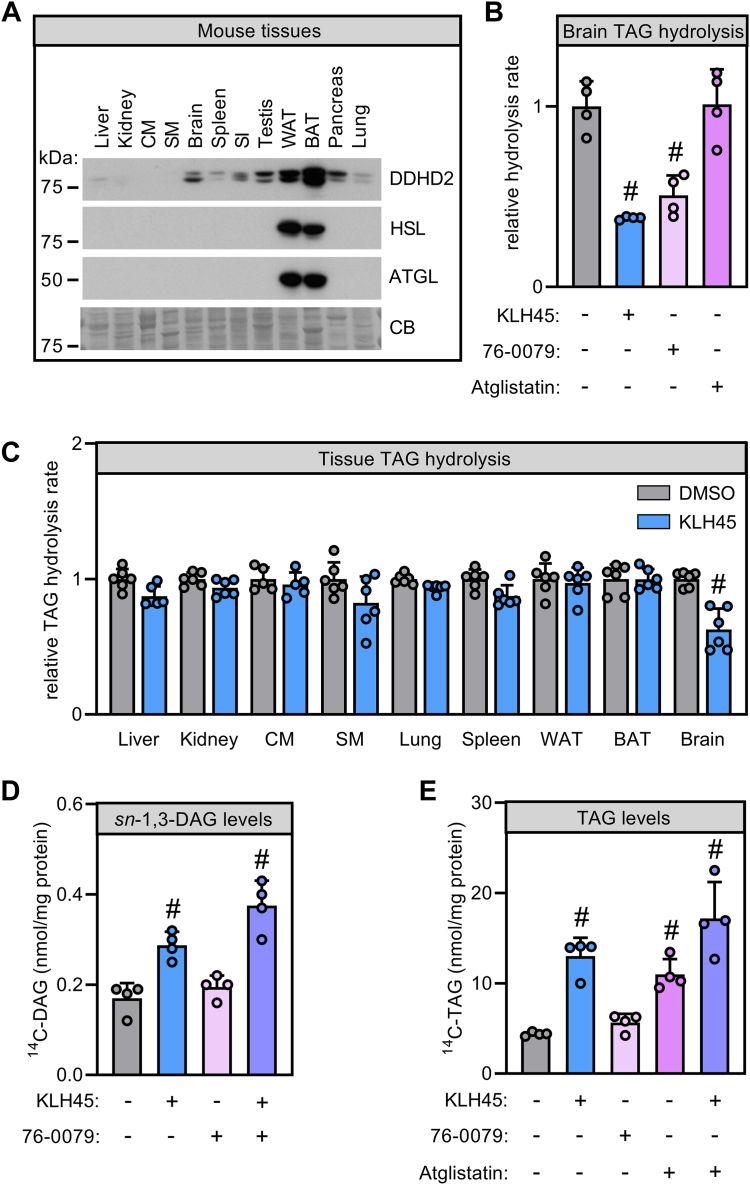
Fig. 5.
Impact of cytosolic lipases on TAG hydrolysis of murine brain and primary cortical neurons. A: Western blotting analysis of cytosolic lipase expression in murine tissues. Tissue homogenates of male C57BL/6J were separated by gel electrophoresis, and protein expression of DDHD2, HSL, and ATGL was detected by immunoblotting. B: Inhibition of endogenous lipase activities in murine brain homogenates. Brain extracts were incubated with TAG substrates and small molecule inhibitors as indicated, and the release of fatty acids was quantified. C: Inhibition of DDHD2 activity in murine tissue homogenates. Tissue extracts were incubated with TAG substrates and KLH45 or DMSO as indicated, and the release of fatty acids was quantified. D: Levels of sn-1,3-DAG and (E) TAG in primary cortical neurons after lipase inhibition. Primary cortical neurons were incubated with 14C-oleic acid and lipase inhibitors as indicated, and radioactivity in sn-1,3-DAG and TAG, respectively, was quantified. Data are expressed as means +SD. Statistical significance was assessed by (C) multiple t-tests or (B, D, E) ANOVA (n = 4–6; #, P < 0.05). TAG, triacylglycerol; ATGL, adipose triglyceride lipase; BAT, brown adipose tissue; CM, cardiac muscle; DDHD2, DDHD domain-containing 2; DAG, diacylglycerol; HSL, hormone sensitive lipase; SI, small intestine; SM, skeletal muscle; TAG, triacylglycerol; WAT, white adipose tissue.