Fig. 4.
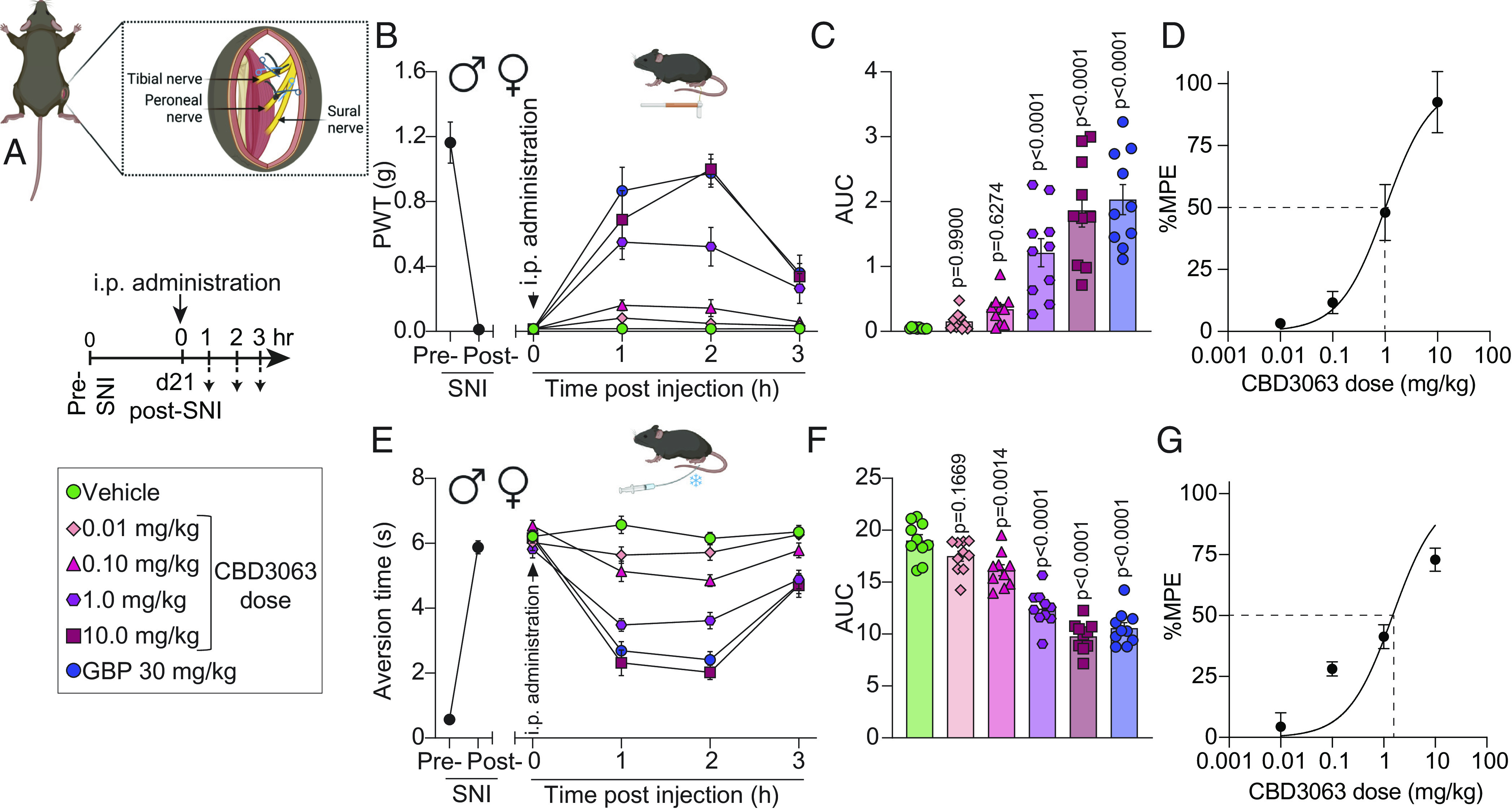
CBD3063 reverses mechanical and cold allodynia in two models of neuropathic pain. (A) SNI model schematic. Timeline and treatment conditions indicated. (B) Baseline (BL) paw withdrawal threshold (PWT) measurements were conducted before (pre-SNI) and after (post-SNI) nerve injury. Dose–response curves of single i.p. injections of vehicle, CBD3063, or GBP were measured from 0 to 3 h post injection on day 21 post-SNI. n = 10 mice. Results were compared using two-way ANOVA, factors; time*treatment, and Tukey post hoc test. (C) Quantification of area under the curve (AUC) in panel B from 0 to 3 h. CBD3063 (1 to 10 mg/kg) reversed SNI-induced mechanical allodynia at a similar fashion as GBP. P values as indicated; one-way ANOVA with the Dunnett post hoc test. n = 10 mice. (D) Dose–response curve analysis for the antinociceptive activity induced by CBD3063. MPE (%) = Antinociception as a percentage of the maximum possible effect. (E) BL measurements of aversion time to acetone stimulation were conducted before (pre-SNI) and after (post-SNI) nerve injury. Aversion time responses were measured from 0 to 3 h post injection. n = 10 mice. Results were compared using two-way ANOVA, time*treatment, and Tukey post hoc test. (F) Quantification of AUC in panel E between 0 and 3 h. CBD3063 (1 to 10 mg/kg) and GBP exhibited comparable reversal of SNI-induced cold allodynia. P values as indicated; one-way ANOVA followed by the Dunnett post hoc test. n = 10 mice. (G) Dose–response curve analysis for cold aversion induced by CBD3063 as a percentage of the maximum possible effect. For all panels, error bars indicate mean ± SEM, groups composed of 50% males and 50% females. See Dataset S1 for full statistics.
