Figure 1. Transgenic mice overexpressing nmrHas2 are resistant to both spontaneous and induced cancer.
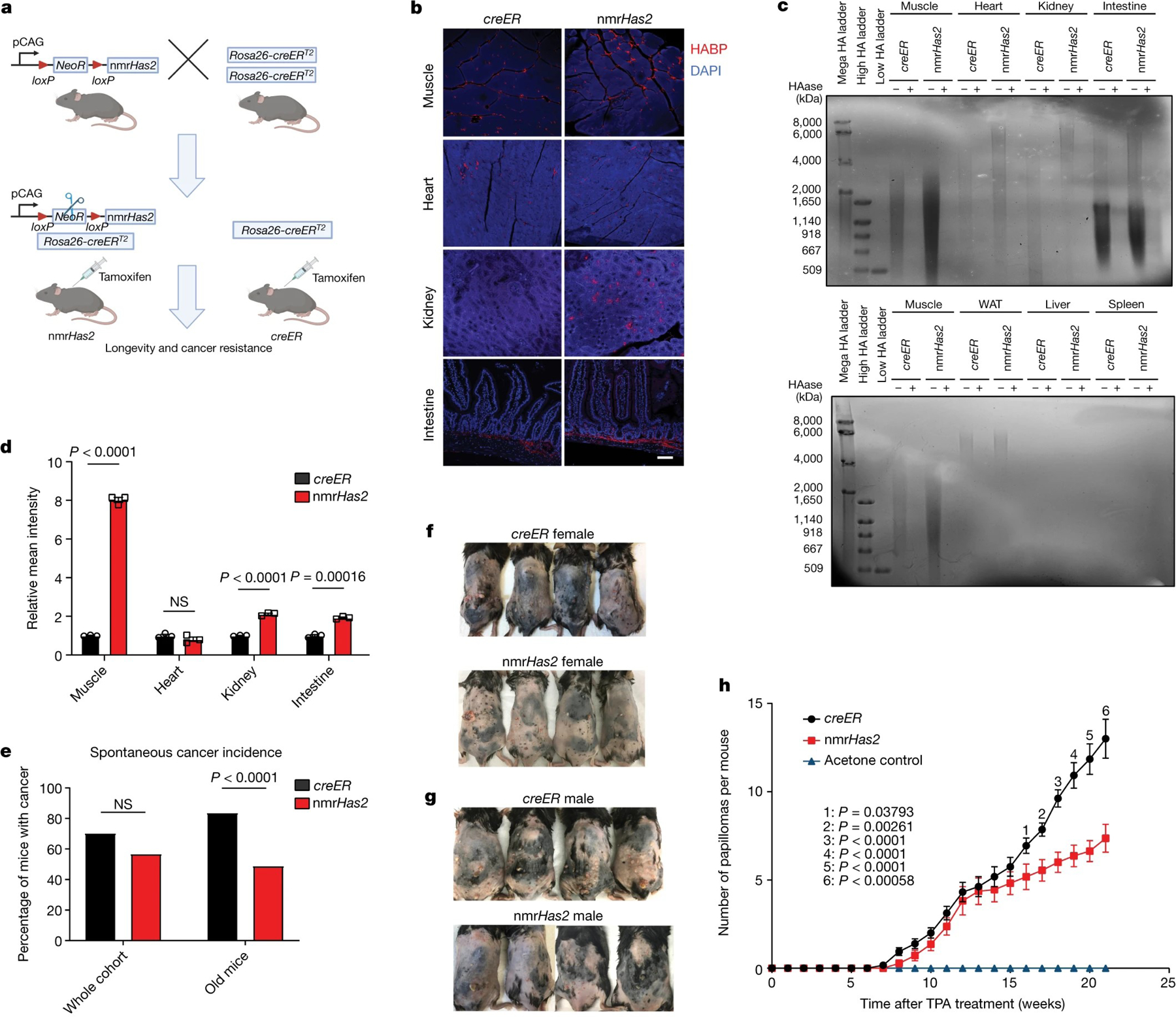
a. The breeding strategy for nmrHas2 mice. Mice heterozygous for the nmrHas2 transgene were bred with mice homozygous for Rosa26-creERT2 to obtain double-heterozygous nmrHas2; creER progeny. Single-heterozygous creER progeny were used as controls. Tamoxifen was injected at 2–3 months of age to induce nmrHas2 expression. creER mice also received tamoxifen.
b. Representative pictures of HABP staining in multiple organs of female mice. Scale bar, 50 μm.
c. Pulse-field gel showing that nmrHas2 mice have higher molecular mass and more abundant HA in multiple tissues (female mice are shown). HA was extracted from 200 mg of pooled tissue from two individuals. HAase-treated samples were run in parallel to confirm the specificity of HA staining. HA from the muscle was loaded onto both gels as a cross reference. WAT, white adipose tissue.
d. Quantification of relative HABP fluorescence intensity shown in b. n = 3 biological replicates (squares).
e. Old nmrHas2 mice (n = 74) have a much lower spontaneous cancer incidence compared with creER mice (n = 81). Pooled female and male mice. Old mice were older than 27 months. Statistical analysis was performed using a two-tailed χ2 test.
f. Representative pictures of female mice after 20 weeks of DMBA/TPA treatment.
g. Representative pictures of male mice after 20 weeks of DMBA/TPA treatment.
h. nmrHas2 mice are more resistant to DMBA/TPA-induced skin papilloma. Pooled female and male mice. n = 7 (acetone treated), n = 13 (creER) and n = 11 (nmrHas2) mice. P values were calculated using two-tailed unpaired t-tests and are indicated in the graphs. NS, not significant. For d, e and h, data are mean ± s.e.m. (d and h) or mean (e).
