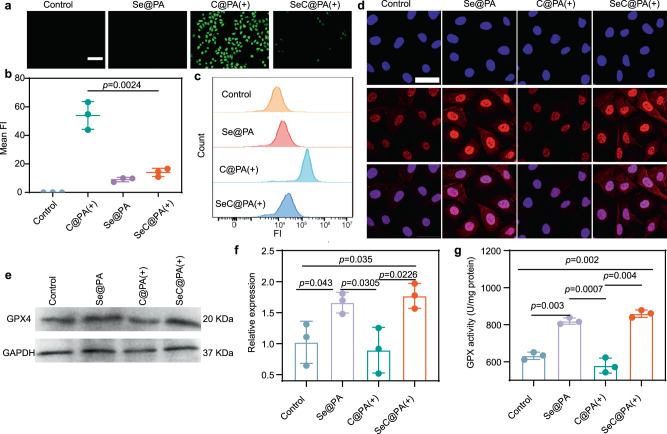
Fig. 4. Anti-inflammatory effect of nanoparticles.
a, b Detection of RS by fluorescence of DCF in the HUVECs incubated with different nanoparticles under 660 nm irradiation (0.2 W/cm2) for 3 min (n = 3 biologically independent samples; mean ± SD). Scale bar is 500 μm. c Intracellular DCF fluorescence intensity of HUVECs with different groups analyzed by flow cytometry. d Representative images of GPX4 staining of HUVECs after different treatments. Scale bar is 200 μm. Three independent experiments were performed and representative results are shown. e, f Expression level of GPX4 in the HUVECs determined by western blotting after treatments (n = 3 biologically independent samples; mean ± SD). The experiment in e was repeated three times with similar results. g Activity of GPX4 treated with different groups (n = 3 biologically independent samples; mean ± SD). Statistical significance was analyzed via one-way ANOVA with a Tukey post-hoc test. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. Se@PA: Se-PDA-LA nanoparticles; C@PA(+): Ce6-PDA-LA nanoparticles under 660 nm irradiation (0.2 W/cm2) for 3 min; SeC@PA(+): Se-Ce6-PDA-LA nanoparticles under 660 nm irradiation (0.2 W/cm2) for 3 min.