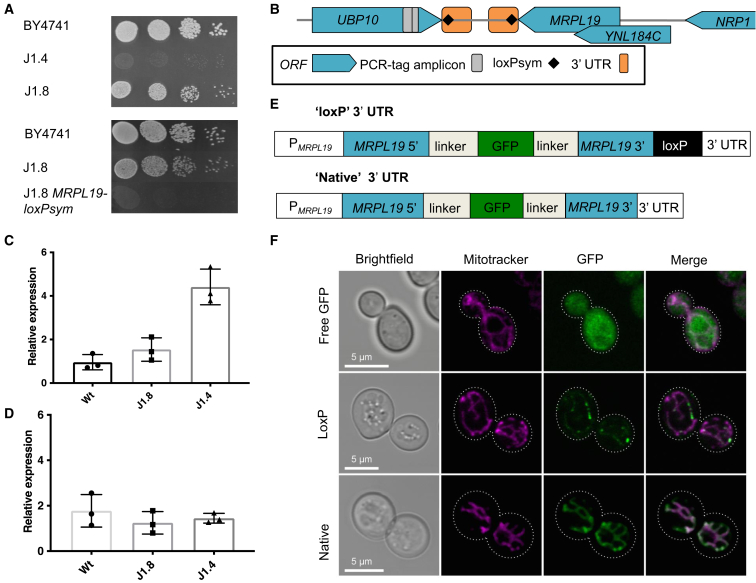
Figure 2.
Chunk J1 growth defect and gene expression analysis
(A) YPG fitness test of chunk J1 integrants 4 and 8 (strains 39 and 40; Table S1) and the wild-type (BY4741, strain 1; Table S1) and wild-type, J1 integrant 8, and J1 integrant 8 with the MRPL19 loxPsym (strain 79; Table S1). Plates were incubated at 30°C for 3–4 days prior to imaging and are representative of two repeated experiments.
(B) Genetic context of the MRPL19 gene and the surrounding synthetic chromosome design features.
(C and D) RT-qPCR of the MRPL19 (C) and NPR1 (D) genes was carried out on cDNA from BY4741 (wild-type), repaired synXIV (J1.8, strain 40; Table S1), and growth defect synXIV (J1.4, strain 39; Table S1) strains. Expression was normalized to the ALG9 gene using the modified Livak method as previously described.23 Bars and error bars represent mean and standard deviation from three biological replicates. Individual expression values of replicates are also shown.
(E) Two synthetic MRPL19 promoter-gene-3′ UTR constructs were designed with a super-folder GFP encoded in the middle of the native ORF, separated by peptide linkers. One version contained a loxPsym motif 3 bp after the stop codon (termed loxP), while the second version contained no loxP within the native 3′ UTR (termed native).
(F) BY4741 strains expressing either of these two constructs (strains 49 and 48) or a cytosol-localized GFP (termed free GFP,24 strain 50; Table S1) were grown in the presence of 100 nM Mitotracker Red (Thermo Fisher) to stain mitochondria. An Olympus FV 1000 confocal microscope was used to visualize yeast cells with bright field, MitoTracker, and GFP signals.