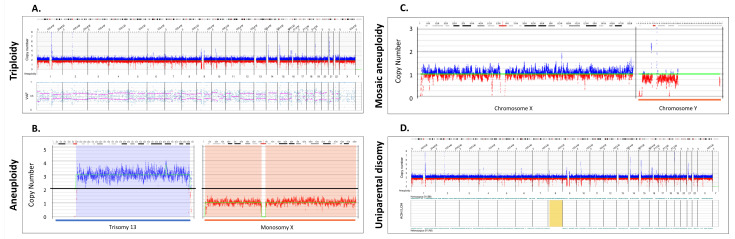
Figure 1.
Whole chromosomal abnormalities and absence of heterozygosity. (A) A triploid genome (69,XXX, Sample 51) showing CN profile and variant allele fraction profiles (VAF). OGM software (Bionano Access v.1.7) automatically quantifies VAF for all variants and constructs a plot depicting the genome wide distributions, shown in the bottom part of (A). In cases of a triplication the VAF are distributed differently compared to diploid chromosomes: VAF around 1 for variants present in 3 alleles, 0.67 for variants present in 2 alleles, and 0.33 for variants present in only 1 allele (VAF around 0.67 and 0.33 indicated by pink lines, see also Supplementary Figure S1A). (B) Copy number profile displaying two aneuploidies: trisomy 13 (Sample 48) and monosomy X (Sample 49). The Y axis represents the copy number measurement with the black line centered at two copies. Blue lines above the baseline represent gains and red losses. The cytobands for each of the chromosomes are displayed on the top. (C) Copy number profile displaying a mosaic loss of the Y chromosome (Sample 47). (D) AOH and CNV profiles displaying regions on chromosome 8 that do not have heterozygous variants indicating a potential uniparental disomy, highlighted in yellow (Sample 52).