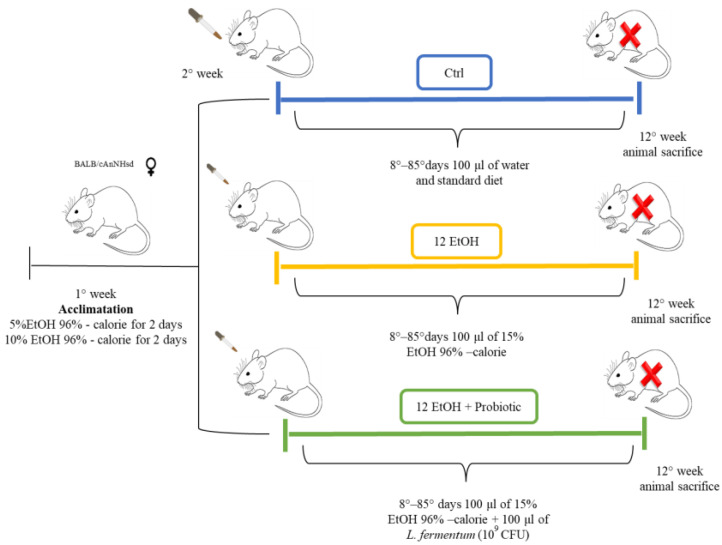
Figure 1.
Animal model and diet. The control group (Ctrl, blue) received only the standard diet (without ethanol or probiotic) for the entire duration of the protocol (12 weeks). For the experimental mice, EtOH 96% was added to account for 15% of total calories in the diet. To acclimate the mice to the alcohol containing diet, they were given 5% EtOH-calorie content for 2 days, then 10% EtOH-calorie content for 2 days, and lastly 15% EtOH-calorie content for 12 weeks (12 EtOH, yellow). In addition, 12 EtOH + Probiotic (green) mice received orally the probiotic L fermentum LF31 (Bromatech S.r.l., Milan, Italy), 109 CFU per animal per day, 5 days per week until the end of the experiments. The pertinent EtOH dose was diluted in water to a final volume of 100 μL. This volume was orally administered to the mice every day using a pipette and a tip, and after 20 min, the mice were fed with the probiotic in the same manner. At the end of the treatment the mice were euthanized (red X letter) and their brain and intestine were then dissected, fixed in formalin, and embedded in paraffin for further analyses [14]. Abbreviations: CFU, colony-forming units; Ctrl, control group; EtOH, ethanol; L. fermentum LF31, Lactobacillus fermentum LF31.