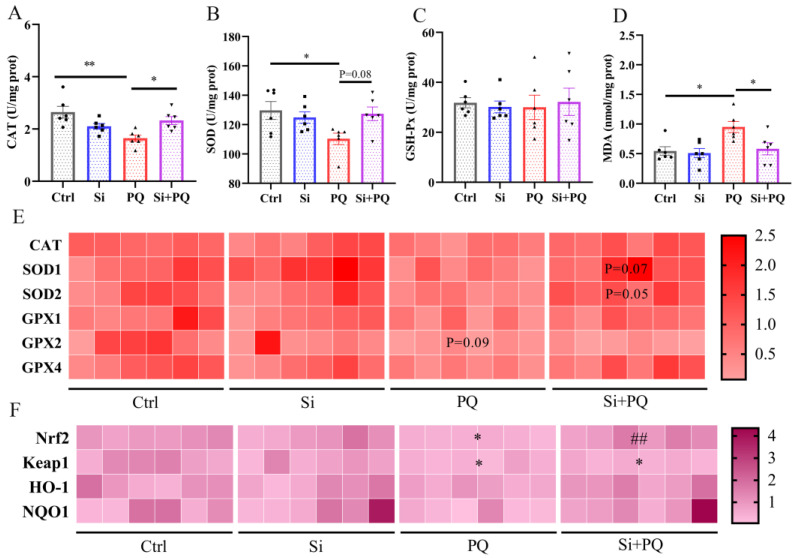
Figure 2.
Dietary silybin supplementation alleviated paraquat-induced intestinal oxidative stress in piglets. The activities of CAT (A), SOD (B), GSH-Px (C), and the level of MDA (D) in the jejunum. The heat maps of the mRNA abundance for antioxidant enzyme genes (E) and Nrf2/Keap1 signaling pathway genes (F), * p < 0.05 vs. Ctrl group; ## p < 0.01 vs. PQ group. Data are expressed as mean ± standard error. * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01. Ctrl = basal diet group treated with saline; Si = silybin diet group treated with saline; PQ = basal diet group treated with paraquat; Si + PQ = silybin diet group treated with paraquat; CAT = catalase; SOD = superoxide dismutase; GSH-Px = glutathione peroxidase; MDA = malondialdehyde; GPX = glutathione peroxidase; Nrf2 = nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2; Keap1 = kelch-like ECH-associated protein l; HO-1 = heme oxygenase-1; and NQO1 = NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase 1.