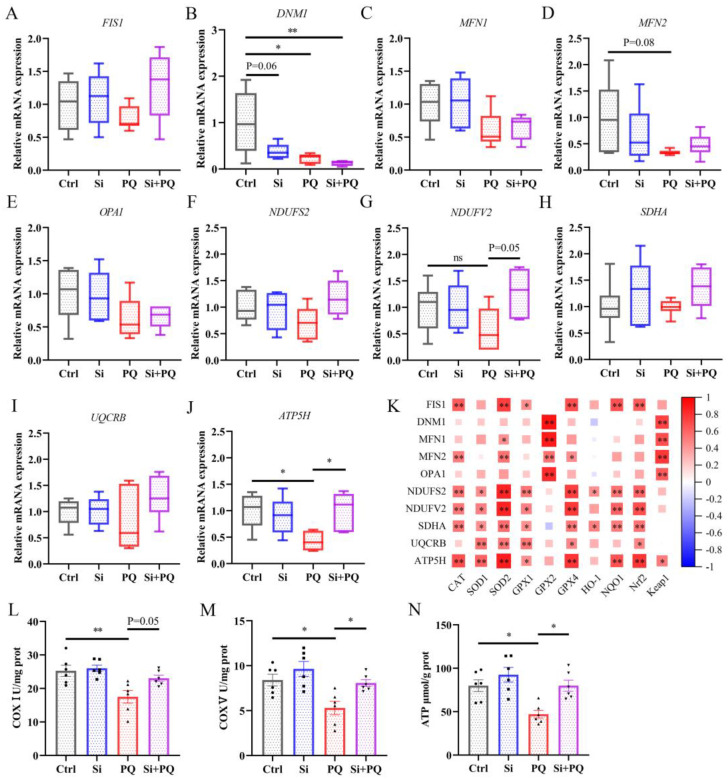
Figure 3.
Dietary silybin supplementation protected against PQ-induced mitochondrial injury. (A–E) The expression of mitochondrial biogenesis genes includes FIS1 (A), DNM1 (B), MFN1 (C), MFN2 (D), and OPA1 (E). The relative mRNA abundance of mitochondrial respiratory chain membrane protein-related genes includes NDUFS2 (F), NDUFV2 (G), SDHA (H), UQCRB (I), and ATP5H (J). The heatmap of Spearman’s correlation between the expression of mitochondrial function-related genes and Nrf2 pathway genes (K). The activities of mitochondrial complex I (L), complex V (M), and ATP level (N) in the jejunum. Data are expressed as mean ± standard error. * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01. Ctrl = basal diet group treated with saline; Si = silybin diet group treated with saline; PQ = basal diet group treated with paraquat; Si + PQ = silybin diet group treated with paraquat; FIS1 = fission; DNM1 = dynamin 1; MFN = mitofusin; OPA1 = mitochondrial dynamin-like GTPase; NDUFS2 = NADH ubiquinone oxidoreductase core subunit S2; NDUFV2 = NADH ubiquinone oxidoreductase core subunit V2; SDHA = succinate dehydrogenase complex flavoprotein subunit A; UQCRB = ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase binding protein; ATP5H = ATP synthase subunit d; CAT = catalase; SOD = superoxide dismutase; GPX = glutathione peroxidase; Nrf2 = nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2; Keap1 = kelch-like ECH-associated protein l; HO-1 = heme oxygenase-1; NQO1 = NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase 1; COX = mitochondrial complex; and ATP = adenosine triphosphate.