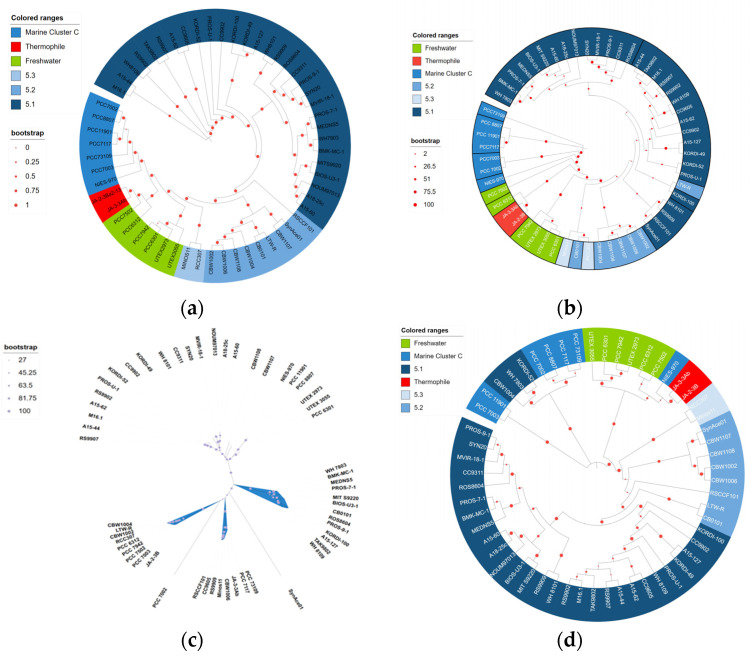
Figure 2.
Systematic evolutionary diversity. Phylogenomic analysis with previously available marine Synechococcus reference genomes placed these within several clades, including 5.1, 5.2, 5.3 [17], Marine cluster C [18], thermophile, and freshwater. (a) Circular phylogenetic tree based on the complete genome sequence. The phylogenetic tree is from GTDB, with branch lengths reflecting phylogenetic information as inferred from the concatenation of 120 marker genes; (b) circular phylogenetic tree based on 16S rRNA; (c) unrooted circular phylogenetic tree based on peroxiredoxin, where the blue color represents the phylogenetic group to which the strain belongs; (d) circular phylogenetic tree analysis of cytochrome C oxidase subunit I sequences.