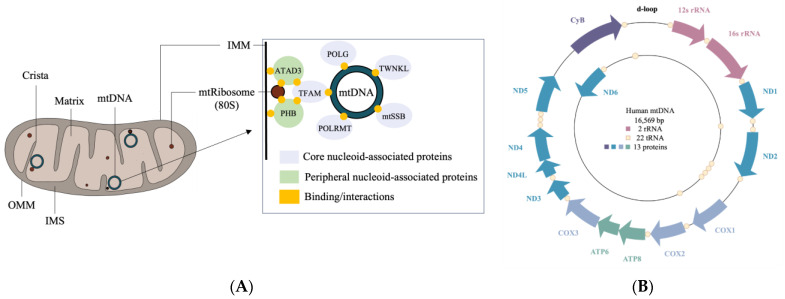
Figure 1.
The structure of and genomic properties of mitochondria. (A) Mitochondrial compartments include the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM); the intermembrane space (IMS); the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM), which folds to form cristae; and a matrix that houses mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) and 80S ribosomes (mtRibosomes). Inset: mtDNA binds core proteins that interact with peripheral proteins, mtRibosomes, and the IMM, forming a nucleoid. Core proteins include transcription factor A (TFAM), Twinkle (TWNKL), RNA polymerase (POLRMT), single-stranded DNA binding protein (mtSSB), and polymerase subunit gamma (POLG), whereas peripheral proteins include ATPase family AAA domain containing protein 3 (ATAD3) and prohibitin (PHB1 and PHB2). (B) Human mtDNA (16,569 bp) encodes 2 rRNA, 22 tRNA, and 13 proteins that form subunits of oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) complexes, including NADH dehydrogenases (ND1, ND2, ND3, ND4, ND4L, ND5, and ND6), cytochrome c oxidases (COX1, COX2, and COX3), ATP synthases (ATP6 and ATP8), and cytochrome b (CyB).