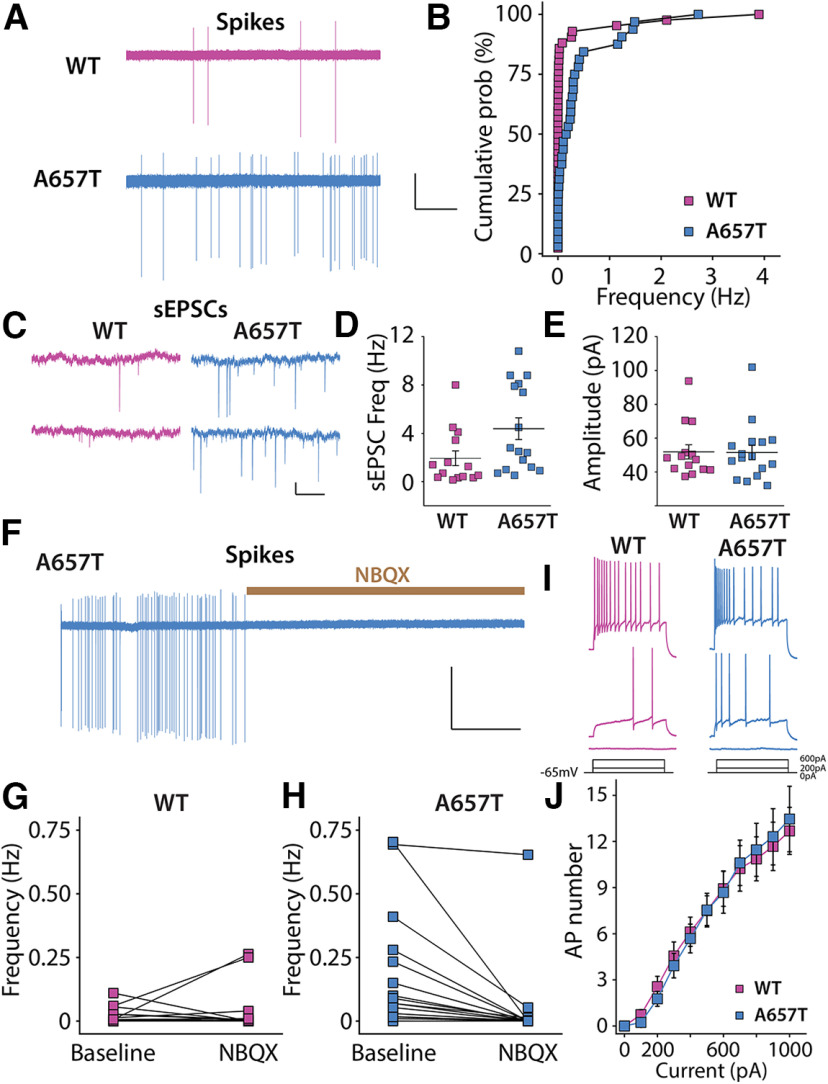
Figure 3.
CA3 neurons are more excitable because of synaptic mechanisms in A657T mice. A, Representative action currents (spikes) recorded from CA3 neurons in cell-attached mode from WT and A657T mice. Calibration: 50 pA, 25 s. B, Cumulative distribution of spike frequency recorded in CA3 neuron from WT and A657T mice. There is an increase in spike firing in A657T mice. C, Example traces of sEPSCs recorded in CA3 neurons in WT and A657T mice. Calibration: 50 pA, 1 s. D, sEPSC frequency in CA3 is elevated in A657T mice. E, Amplitude of sEPSCs is not affected in A657T mice. F, Example continuous trace of spikes recorded in CA3 neurons prior to and after glutamate receptor antagonist application NBQX (50 µm). G, Analysis of spontaneous action current frequencies before and after NBQX in WT and (H) A657T mice. I, Example traces of APs in CA3 neurons initiated by somatic current injection. J, Full frequency I-O curve for AP firing of CA3 neurons with increasing current injection.