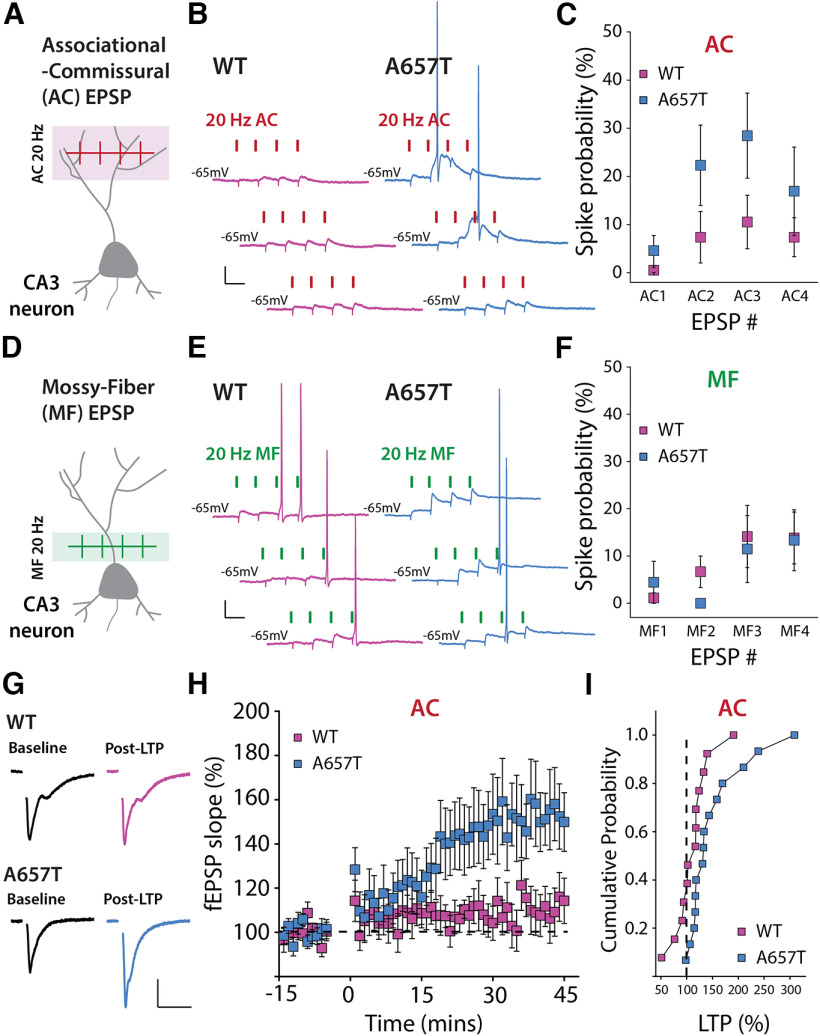
Figure 5.
EPSP-spike coupling and NMDAR-dependent LTP of distal AC synapses is enhanced in A657T mice. A, Diagram representation of AC-EPSP stimulation. B, Representative traces of AC-EPSPs and APs stimulated at 20 Hz in CA3 neurons in WT and A657T mice. Calibration: 10 mV, 50 ms. C, Spike probability at each AC-EPSP during the train of stimuli in recordings from WT and A657T mice. D, Schematic of MF synaptic stimulation. E, Representative MF-EPSPs and APs stimulated at 20 Hz in CA3 neurons. Calibration: 10 mV, 50 ms. F, Spike probability at each MF EPSP during the 20 Hz train in WT and A657T mice. G, Example traces of fEPSPs before (Baseline) and after (Post-LTP) LTP induction in WT (top) and A657T mice (bottom). Calibration: 0.2 mV, 20 ms. H, Time course of LTP of AC fEPSP responses induced at time = 0 using a 4 × 50 Hz burst repeated 10 times at 1 Hz in WT and A657T mice. I, Cumulative distribution for AC LTP in WT and A657T mice.