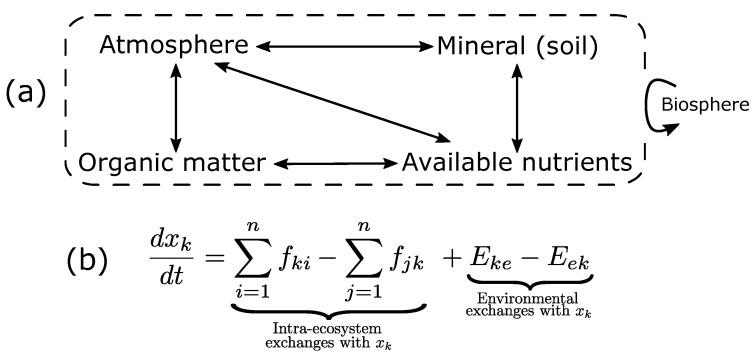
Figure 1.
Compartment model of a terrestrial ecosystem. (a): Ecosystem compartments linked through matter and energy fluxes represented by arrows. Each compartment may be split into several sub-compartments (e.g., organic matter can be split into living and dead organic matter). The dotted box represents ecosystem boundaries, through which the ecosystem is also linked to the whole biosphere through biotic and abiotic processes. Adapted from [50]. (b): A system of ordinary differential equations (ODEs) of n variables for and parameters. With and describing incoming (from i to k) and outgoing (from k to j) fluxes within the ecosystem, respectively, and and describing incoming and outgoing environmental exchanges, respectively [51].