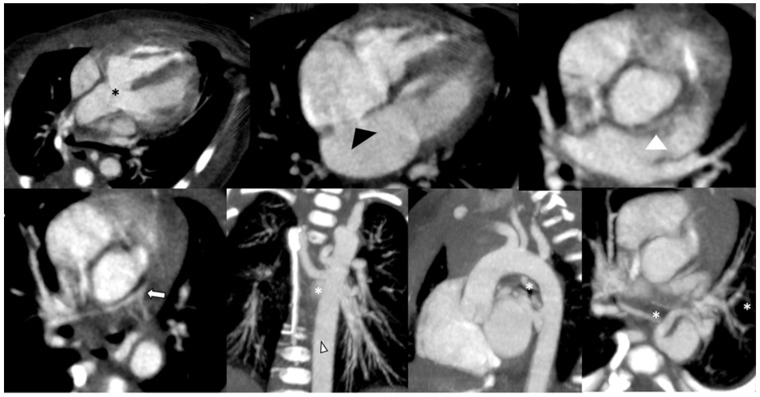
Figure 3.
CCT in a 2-day-old newborn with Tetralogy of Fallot, scanned in sedation and free-breathing at high heart rate (145 bpm), using a low-dose protocol (80 kV) and prospective ECG triggering. The main features are also detected and depicted in the images in multiplanar and curved reformation (MPR-CPR) and maximum intensity projection (MIP): ventricular septal defect and overriding aorta (black asterisk), PFO (black arrowhead), pulmonary valve atresia and pulmonary artery hypoplasia (white arrow), and major aortopulmonary collateral arteries (white asterisks). Despite the very high heart rate, in a low-birth-weight preterm baby (2.3 Kg) scanned at a high heart rate, the left coronary artery is detectable (white arrowhead).