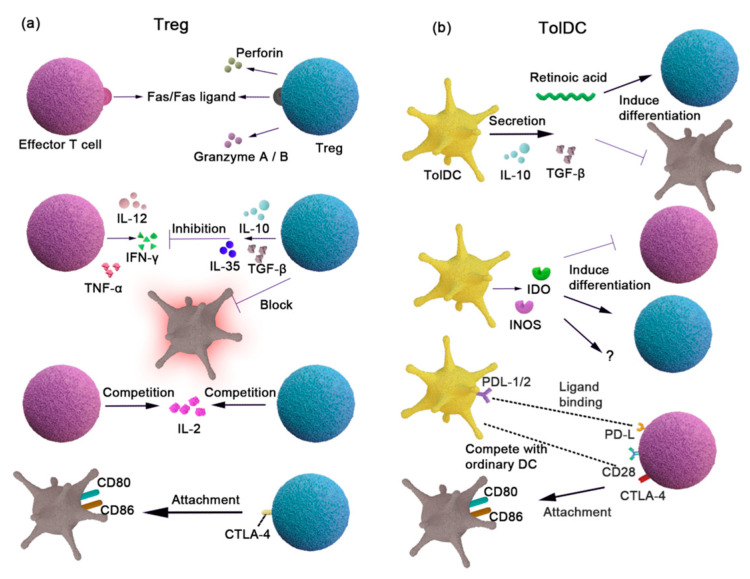
Figure 3.
Tolerability mechanism of Treg and tolDC. (a) The nTreg mediates cell lysis through granzyme A/B and perforin secreted by cell-to-cell interaction, and iTreg mediates cell lysis through Fas/Fas ligand action on specific CD4+ T cells. TGF-β inhibited activated gluten-specific CD4+ T cells and promoted IL-10 secretion. IL-10 inhibits pro-inflammatory factor secretion (such as IFN-γ, IL-12, and TNF-α), blocking wheat toxic protein antigen presentation. This is through the competitive inhibition of IL-2 proliferation to other cells, the upregulation of cAMP, and inhibiting pro-inflammatory gene expression. Treg surface molecular CTLA-4 (CD152) attached to APCs’ stimulus molecules (CD80 and CD86) inhibits intercellular interdependence mechanisms. (b) PD-L1/2 (programmed death-ligand 1/2) and CTLA-4 (cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-related protein 4) are highly expressed on the surface and compete with CD80 and CD86 to bind to CD28 on the surface of other DCS. Secretion of IL-10 and TGF-regulatory effects of T cells and Treg; IDO (indoleamine 2, 3-dioxidase) and iNOS (inducible nitric oxide synthase) are secreted to induce Treg.