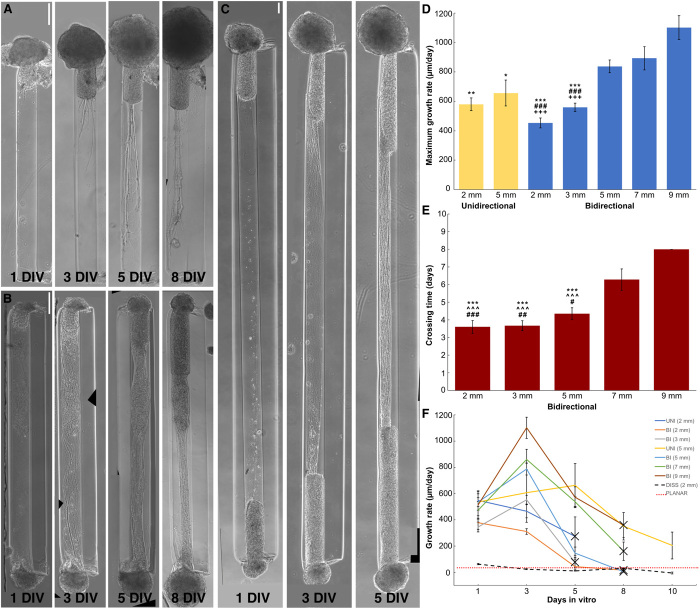
Fig. 2. Axonal growth in aggregate μTENNs over time.
Aggregate μTENNs grow rapidly over 1 to 8 DIV; unidirectional μTENNs (A) project axons to the opposing terminal, while bidirectional μTENNs (B) axons cross the microcolumn and synapse with the opposing aggregate. Representative 2-mm μTENNs shown at 1, 3, 5, and 8 DIV. (C) Representative 5-mm μTENN shown at 1, 3, and 5 DIV. (D) Average maximum growth rates across μTENN lengths. In general, longer bidirectional μTENNs displayed higher peak growth rates. Symbols indicate a significantly lower maximum growth rate than a specific group: 9-mm bidirectional (*), 7-mm bidirectional (#), and 5-mm bidirectional (+) μTENNs, respectively. Symbol count denotes significance level (1: P < 0.05; 2: P < 0.01; 3: P < 0.001). (E) Average crossing times across μTENN groups. Similarly, longer constructs tended to take more time to develop. Unidirectional (5 mm) μTENNs did not fully cross the microcolumn by 10 DIV and were not included. Symbols and symbol counts match those described in (D), with the addition of significance versus 8-mm bidirectional (^). (F) Growth rates for unidirectional, bidirectional, and dissociated μTENNs at 1, 3, 5, 8, and 10 DIV. Growth rates were quantified by identifying the longest neurite from an aggregate in phase microscopy images (×10 magnification) at the specified time points. Crosses indicate axons crossing the length of the microcolumn (unidirectional) or connecting between aggregates (bidirectional). Error bars denote SEM. Scale bars, 200 μm.