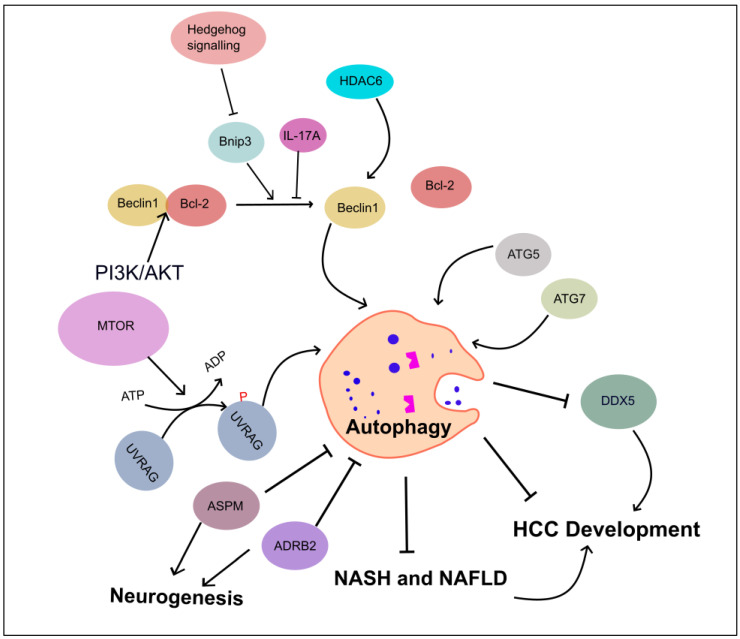
Figure 4.
Role of autophagy-associated genes in inhibiting HCC development. This figure illustrates the regulators of autophagy in HCC development and progression. These regulatory mechanisms include Beclin1, HDAC6, autophagy-related gene proteins (ATG5 and ATG7), UVRAG, and SMURF1-mediated UVRAG ubiquitination promoting HCC. IL-17A inhibits the dissociation of Becline1/Bcl-2 complex, and PI3K/AKT enforces binding between Bcl-2 and Beclin1. ASPM and ADRB2 proteins are involved in neuronal circuit, leading to autophagy inhibition. Autophagy suppresses DDX5, leads HCC, and curtails the progression of NASH and NAFLD to HCC. Abbreviations: Adrenergic receptor beta-2 (ADRB2), Abnormal spindle-like microcephaly-associated protein (ASPM), DEAD-box helicase 5 (DDX5), and Histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6).