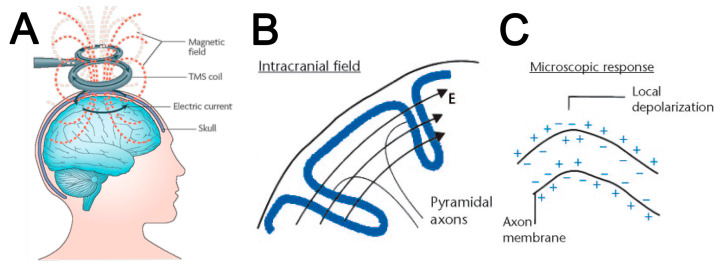
Figure 1.
Overview of electromagnetic induction in TMS: (A) A brief pulsed current flows through a coil generating a magnetic field, which passes through the skull and induces a secondary current, which stimulates the brain. Image adapted from [9], with permission. (B) The electric field (E) within the brain runs through cortical folia essentially perpendicular to the descending pyramidal neuron axons. Image adapted from [10], with permission. (C) Microscopically, the secondary current can locally alter the axon membrane potential and therefore activate neuronal firing (image adapted from [10], with permission).