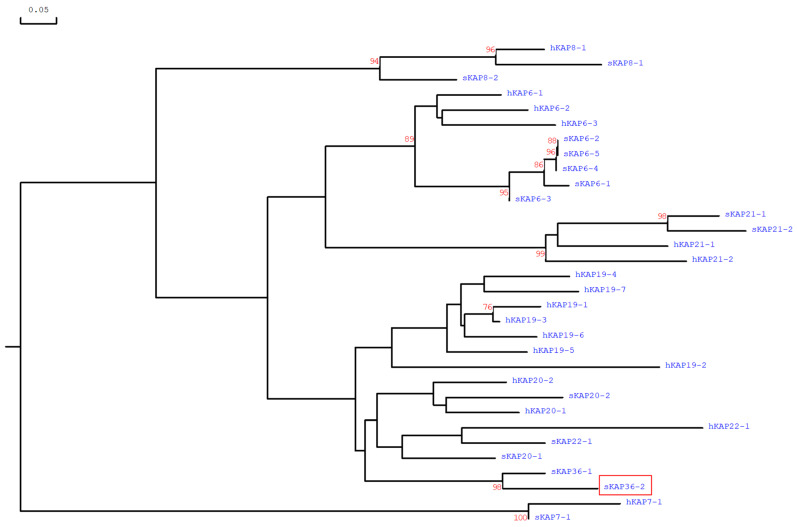
Figure 2.
A phylogenetic tree created based on the anticipated amino acid sequences for ovine KAP36-2 and all the other high-glycine-tyrosine KRTAPs detected in sheep and humans to date. The numbers at the forks denote the bootstrap confidence values and only those equal to or higher than 70% are presented. The scale bar indicates a rate of 0.05 amino acid substitutions per site. The ovine and human sequences are identified with the prefixes “s” and “h”, respectively. The newly identified ovine KAP36-2 sequence is shown in a red frame. Other sequences were retrieved from GenBank with accession numbers: NM_001193399 (sKAP6-1), KT725832 (sKAP6-2), KT725837 (sKAP6-3), KT725840 (sKAP6-4), KT725845 (sKAP6-5), X05638 (sKAP7-1), X05639 (sKAP8-1), KF220646 (sKAP8-2), MH243552 (sKAP20-1), MH071391 (sKAP20-2), KX377616 (sKAP22-1), MK770620 (sKAP36-1), NM_181602 (hKAP6-1), NM_181604 (hKAP6-2), NM_181605 (hKAP6-3), AJ457063 (hKAP7-1), AJ457064 (hKAP8-1), AJ457067 (hKAP19-1), NM_181608 (hKAP19-2), NM_181609 (hKAP19-3), NM_181610 (hKAP19-4), NM_181611 (hKAP19-5), NM_181612 (hKAP19-6), NM_181614 (hKAP19-7), NM_181615 (hKAP20-1), NM_181616 (hKAP20-2), NM_181619 (hKAP21-1), NM_181617 (hKAP21-2), and NM_181620 (hKAP22-1).