Abstract
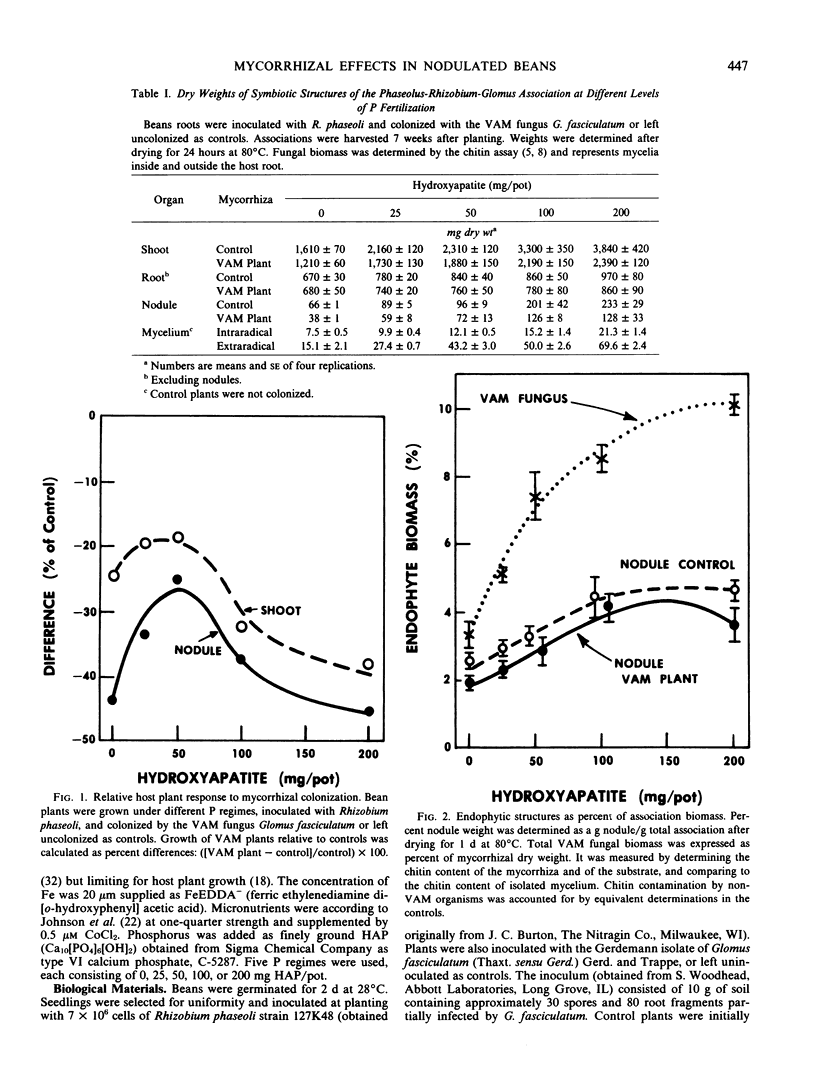
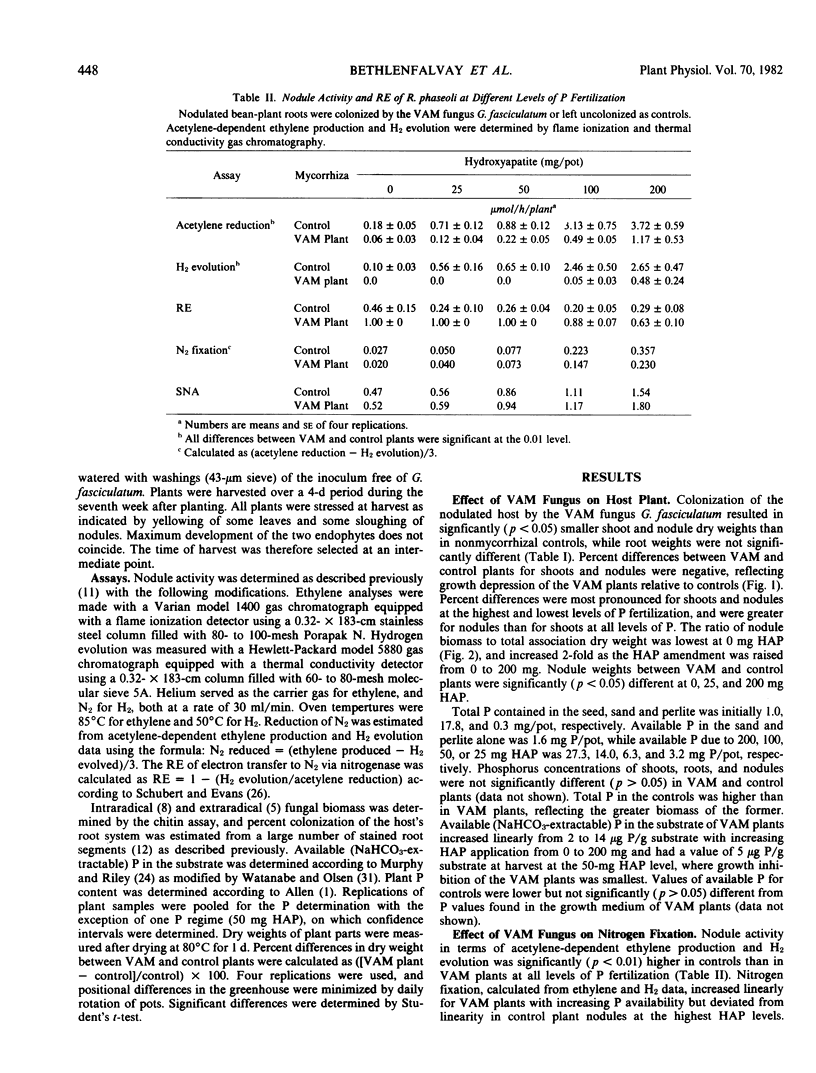
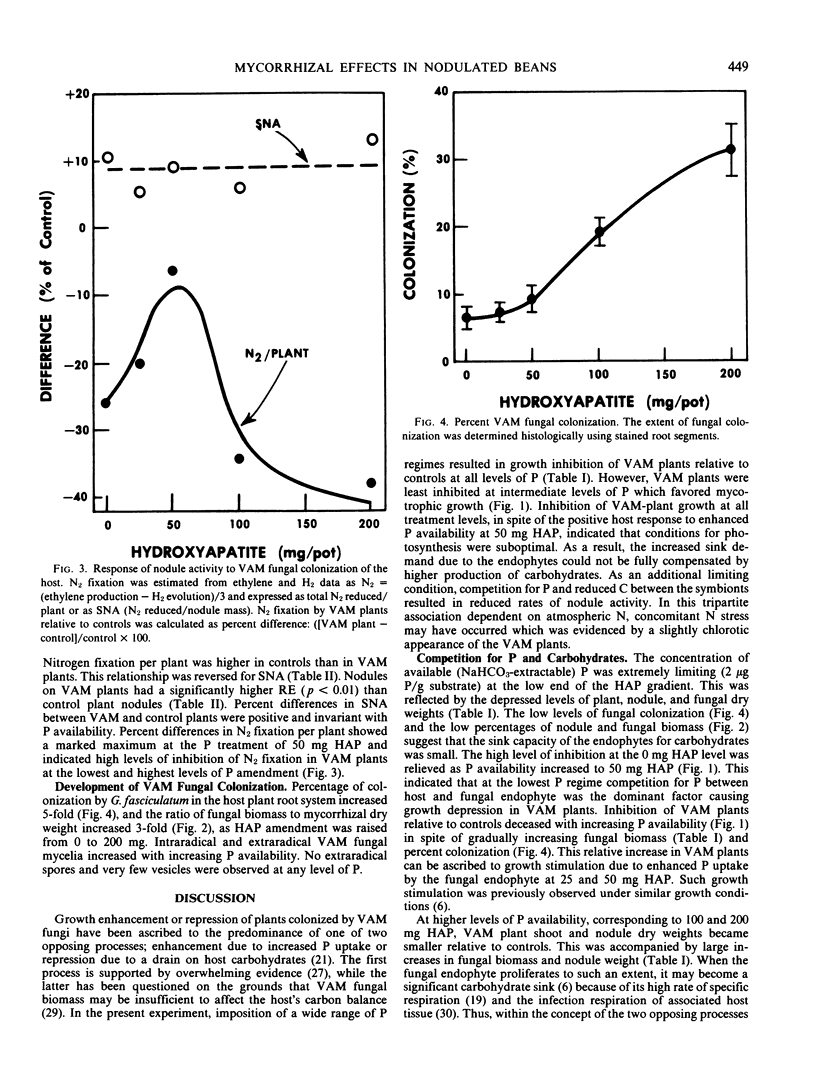
Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L. cv. Dwarf) roots were inoculated with Rhizobium phaseoli and colonized by the vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal (VAM) fungus Glomus fasciculatum Gerd. and Trappe or left uncolonized as controls. The symbiotic associations were grown in an inert substrate using 0, 25, 50, 100, or 200 milligrams hydroxyapatite (HAP) (Ca10[PO4]6[OH]2) per pot as a P amendment. Plant and nodule dry weights and nodule activity increased for both VAM and control plants with increasing P availability, but values for VAM plants were significantly lower in all parameters than for controls. Inhibition of growth and of N2 fixation in VAM plants was greatest at the lowest and highest P regimes. It was smallest at 50 milligrams HAP, where available P at harvest (7 weeks after planting) was 5 micrograms P per gram substrate. At this level of P availability, the association apparently benefited from increased P uptake by the fungal endophyte. Percent P values for shoots, roots, and nodules did not differ significantly (p > 0.05) between VAM and control plants. The extent of colonization, fungal biomass, and the fungus/association dry weight ratio increased several fold as HAP was increased from 0 to 200 milligrams. It is concluded that intersymbiont competition for P and photosynthate was the primary cause for the inhibition of growth, nodulation, and nodule activity in VAM plants. Impaired N2 fixation resulted in N stress which contributed to inhibition of host plant growth at all levels of P availability.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. J. The estimation of phosphorus. Biochem J. 1940 Jun;34(6):858–865. doi: 10.1042/bj0340858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bethlenfalvay G. J., Abu-Shakra S. S., Phillips D. A. Interdependence of Nitrogen Nutrition and Photosynthesis in Pisum sativum L: II. Host Plant Response to Nitrogen Fixation by Rhizobium Strains. Plant Physiol. 1978 Jul;62(1):131–133. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bethlenfalvay G. J., Abu-Shakra S. S., Phillips D. A. Interdependence of Nitrogen Nutrition and Photosynthesis in Pisum sativum L: II. Host Plant Response to Nitrogen Fixation by Rhizobium Strains. Plant Physiol. 1978 Jul;62(1):131–133. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bethlenfalvay G. J., Norris R. F., Phillips D. A. Effect of Bentazon, a Hill Reaction Inhibitor, on Symbiotic Nitrogen-fixing Capability and Apparent Photosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 1979 Jan;63(1):213–215. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bethlenfalvay G. J., Phillips D. A. Ontogenetic Interactions between Photosynthesis and Symbiotic Nitrogen Fixation in Legumes. Plant Physiol. 1977 Sep;60(3):419–421. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.3.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bethlenfalvay G. J., Phillips D. A. Variation in nitrogenase and hydrogenase activity of alaska pea root nodules. Plant Physiol. 1979 May;63(5):816–820. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.5.816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul E. A., Kucey R. M. Carbon flow in plant microbial associations. Science. 1981 Jul 24;213(4506):473–474. doi: 10.1126/science.213.4506.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharf S. M., Bianco J. A., Tow D. E., Brown R. The effects of large negative intrathoracic pressure on left ventricular function in patients with coronary artery disease. Circulation. 1981 Apr;63(4):871–875. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.63.4.871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert K. R., Evans H. J. Hydrogen evolution: A major factor affecting the efficiency of nitrogen fixation in nodulated symbionts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1207–1211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strain L., Dubois E. L. Small inclusions in the cytoplasm of leukocytes in LE cell tests. J Rheumatol. 1978 Winter;5(4):365–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinker P. B. Effects of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizas on higher plants. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1975;(29):325–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. E., Phillips D. A. Effect of irradiance on development of apparent nitrogen fixation and photosynthesis in soybean. Plant Physiol. 1980 Nov;66(5):968–972. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.5.968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


