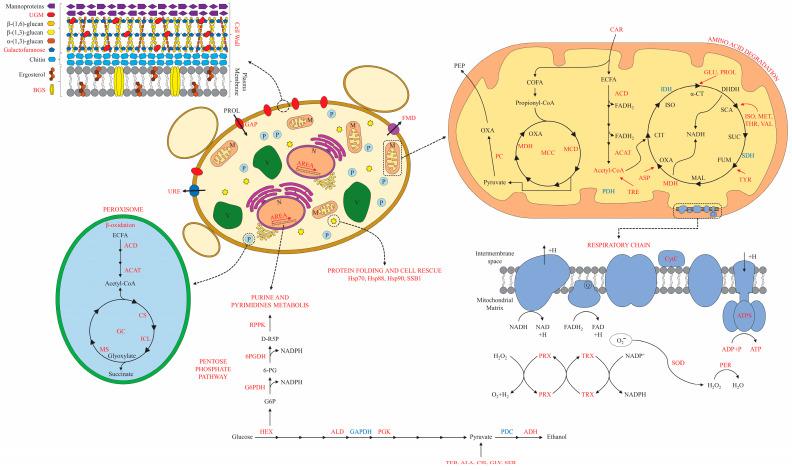
Figure 2.
General overview of P. lutzii metabolism under NCR conditions. The metabolic pathways were determined based on the molecules identified by proteomic analysis in NCR-proline conditions. In red and blue, the molecules that were up-regulated and down-regulated, respectively, in NCR conditions are shown. Abbreviations: 6-PGDH: 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase; ACAT: acetyl-CoA acyltransferase; ACD: acyl-CoA dehydrogenase; ADH: alcohol dehydrogenase; ALA: alanine; ALD: aldolase; AREA: transcription factor AreA; ASP: asparagine; CAR: carnitine O-acetyltransferase; CIS: cysteine; COFA: odd-chain fatty acids; CS: citrate synthase; CytC: cytochrome C; DHDH: dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase; ECFA: even-chain fatty acids; FMD: formamidase; G6PDH: glucose-6-phosphate 1-dehydrogenase; GAP: general amino acid permease; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; GC: glyoxylate cycle; GLI: Glycine; GLU: glutamate; HSP70: heat shock protein 70; HSP88: heat shock protein Hsp88; HSP90: heat shock protein Hsp90; HX: hexokinase; ICL: isocitrate lyase; IDH: isocitrate dehydrogenase; ISO: isoleucine; MCC: methylcitrate cycle; MCD: 2-methylcitrate dehydratase; MDH: malate dehydrogenase; MET: methionine; MS: malate synthase; OXA: oxaloacetate; PC: pyruvate carboxylase; PDC: pyruvate decarboxylase; PDH: pyruvate dehydrogenase; PEP: phosphoenolpyruvate; PER: peroxidase; PGK: phosphoglycerate kinase; PRO: proline; PRX: mitochondrial peroxiredoxin; RPPK: ribose-phosphate pyrophosphokinase; SDH: succinate dehydrogenase; SER: serine; SOD: superoxide dismutase; SSB1: heat shock protein SSB1; THR: threonine; TRX: thioredoxin. TYR: tyrosine UGM: UDP-galactopyranose mutase; URE: urease; VAL: valine.