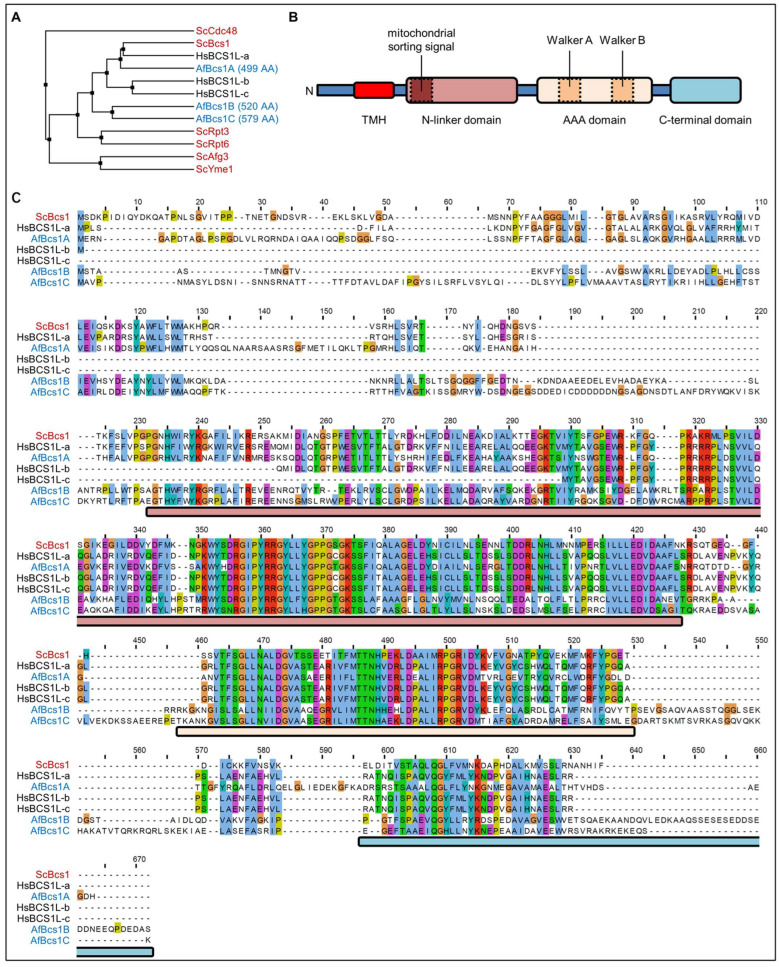
Figure 1.
A. fumigatus encodes three homologs of S. cerevisiae Bcs1 and H. sapiens BCS1L. (A) Average distance tree and alignment of the protein sequences of S. cerevisiae Bcs1 (ScBcs1), the three H. sapiens BCS1L isoforms (HsBCS1L-a, -b, and -c), and the three ScBcs1/HsBCS1L homologs encoded in the genome of A. fumigatus (AfBcs1A, AfBcs1B, AfBcs1C) as well as of closely related S. cerevisiae AAA proteins (ScCdc48, ScRpt3, ScRpt6, ScAfg3, and ScYme1). Amino acid (AA) lengths of A. fumigatus homologs are annotated next to the respective protein names. The average distance tree was generated with BLOSUM62. (B) Schematic representation of the Bcs1 structure featuring a transmembrane domain near the N terminus, a mitochondrial sorting signal in the N-linker domain, the conserved Walker A and Walker B motifs in the AAA domain, plus the so far uncharacterized C-terminal domain. (C) Alignment (T-Coffee; Clustal color scheme) of the protein sequences of S. cerevisiae, H. sapiens, and A. fumigatus Bcs1 homologs. The approximate regions encompassing the domains indicated in (B) are highlighted in the respective colors.