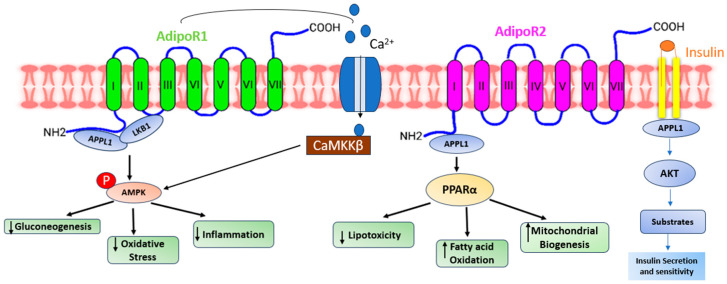
Figure 1.
A presentation demonstrating the diverse pathways through which adiponectin receptors exert their functions. Adiponectin engages with its receptors to initiate various signaling pathways. AdipoR1 enhances calcium influx, leading to the activation of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase β (CaMKKβ) and subsequent downstream kinases. AdipoR1- and R2-dependent signaling are mediated by adaptor protein phosphotyrosine interaction (APPL) 1, which allows LKB1 to translocate from the nucleus to the cytoplasm and activate AMPK, ceramidase activity, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha (PPAR-α). Activation of AMPK reduces gluconeogenesis, oxidative stress, and inflammation. On the other hand, activation of PPAR-α reduces lipotoxicity and inflammation and increases fatty acid oxidation. All these effects ultimately improve glycemic status.