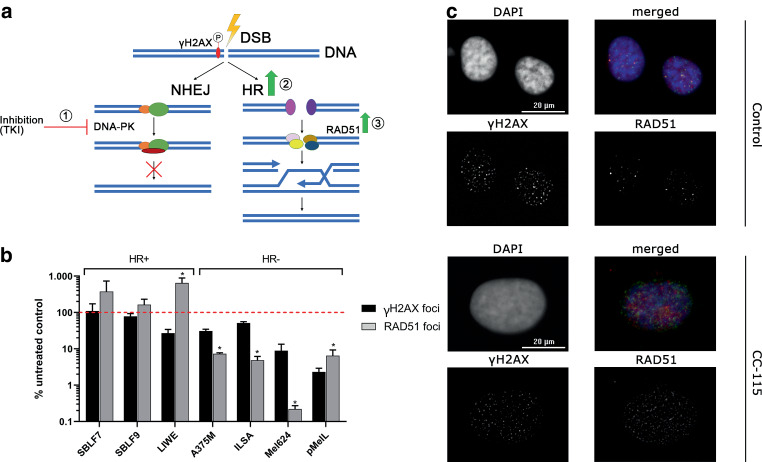
Fig. 4.
Capability of melanoma and fibroblast cell lines to undergo essential DNA damage repair by homologous recombination. Irradiation could lead to DSB, marked by phosphorylation of histone H2AX. a DSB can be repaired via NHEJ or HR. The NHEJ pathway was blocked by inhibition of the central protein DNA-PK, an essential protein in the signal cascade of NHEJ, by treating the cells with CC-115 (①). Since there is evidence that tumor cell lines often harbor mutations in the HR pathway, we forced them to use this repair pathway by treating the cell with a DNA-PK inhibitor. After irradiation (1 × 10 Gy), cells are forced to use the alternative pathway HR (②) associated with RAD51, a key player in HR. Upregulation of RAD51 (③), while forcing cells to HR, can be used to determine HR efficiency. Stable or decreasing RAD51 expression suggests an HR deficiency. b Analysis of RAD51 (grey bars) and yH2AX (black bars) foci of SBLF9, SLBLF7 (healthy control) and five melanoma cell lines after 10 Gy irradiation and treatment of cells with the DNA-PK inhibitor for 48 h. Untreated samples were set as 100%, as represented by the red dashed line. Cells with an increasing number of RAD51 foci after blocking NHEJ were defined as HR proficient (SBLF7, SBLF9, and LIWE), whereas cells with a decreasing number were defined as HR deficient (ILSA, A375M, Mel624, and pMelL). Each value represents mean ± SD (n = 3). Significance was determined by one-tailed Mann–Whitney U test; *p ≤ 0.050. c Representative microscope images of melanoma cell line LIWE without treatment and after blockade of NHEJ via DNA-PKi CC-115. Cells were stained with DAPI (nucleus) and primary antibodies mouse anti-γH2AX (1:1500, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) and rabbit anti-Rad51 (1:250, Abcam, Cambridge, UK)