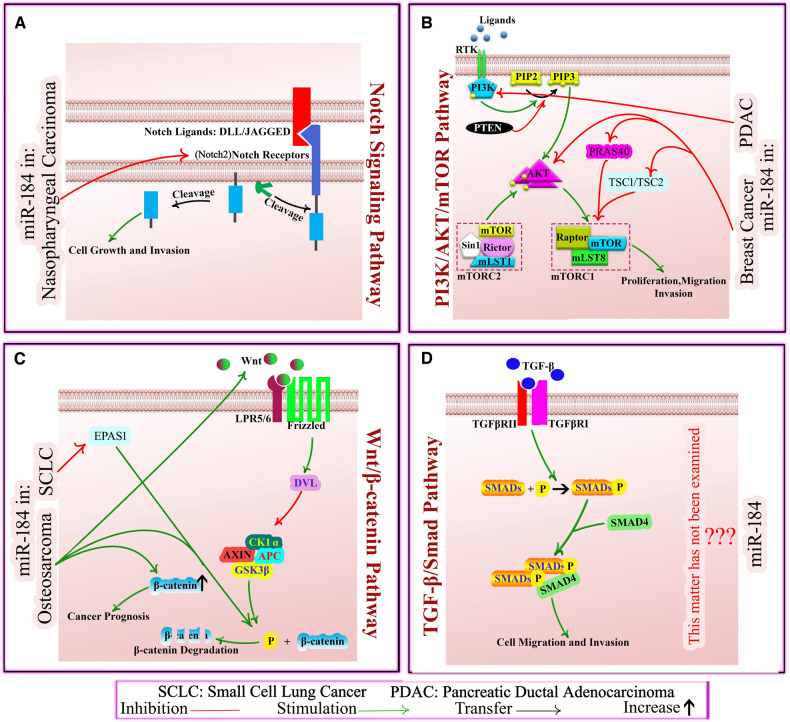
Fig. 2. The mechanistic impact of miR-184 on signaling pathways in some cancers.
A Notch Signaling Pathway. The binding of DLL or JAGGED to Notch receptors leads to the liberation of the NICD, which is subsequently translocated to the nucleus where it interacts with transcription factors. In Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma, miR-184 suppresses Notch2 receptor. B PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway: PI3K generates phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate (PIP3), which activates AKT and it directly targets mTOR, existing in mTORC1 and mTORC2 complexes. PTEN functions by dephosphorylating PIP3. In pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, miR-184 directly targets PI3K and in breast cancer, it may target mTORC1 inhibitors PRAS40 and TSC2 to eventually suppress AKT pathway. C Wnt/β-catenin pathway: In the absence of Wnt ligands, β-catenin is targeted for degradation by a complex comprising Axin, APC, GSK-3β, and CK1. Wnt binding to Frizzled receptors activates the LRP5/6 co-receptor, inhibiting the degrading complex and allows β-catenin to accumulate. In endometrial cancer, miR-184 inhibits Wnt, Frizzled, and DVL, whereas in cervical cancer, it downregulates Wnt. In small-cell lung cancer, miR-184 inhibits EPAS1, β-catenin phosphorylation enhancer. In osteosarcoma, miR-184 increases Wnt and enhances β-catenin levels and phosphorylation status. D TGF-B/Smad pathway: Ligands bind to TGF-B receptors, activating the receptor complex and phosphorylating R-Smads, which then develop complexes with Smad4, translocating into the nucleus to regulate gene expression. The effect of miR-184 on this pathway is unclear. DLL delta-like ligand, PI3K phosphoinositide 3-kinase, PIP3 phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate, mTOR mammalian target of rapamycin, mTORC mammalian target of rapamycin complexes, PTEN phosphatase and tensin homolog, PRAS40 proline-rich Akt substrate of 40 kDa, EPAS1 endothelial PAS domain protein 1, TGF-B transforming growth factor-beta.