Fig. 4. The effects of miR-184 on apoptotic pathways.
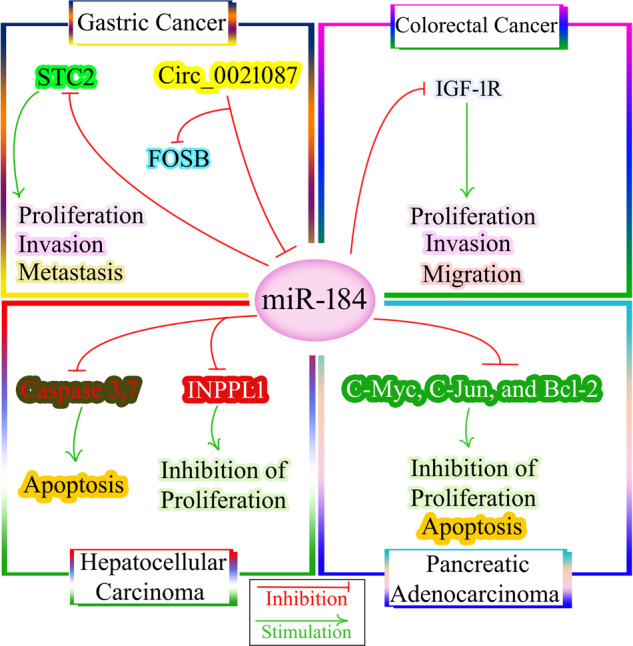
The extrinsic pathway of apoptosis starts by the binding of death ligands (TNF, FasL, and TRAIL) to corresponding receptors, causing recruitment of FADD to the intracellular domain of the death receptor. This triggers the formation of DISC, which itself in a series of reactions activates initial caspase-8 or -10, and then activation of effector caspases-3, -6, and -7 leading to cell death. Caspase-8 or caspase-10 can activate Bid that in turn causes activation of pro-apoptotic proteins Bax and Bak while inhibiting anti-apoptotic members of the Bcl-2 family. In the intrinsic pathway, cellular stress signals trigger conformational changes in Bax and Bak, resulting in release of cytochrome c into the cytoplasm, where it forms the apoptosome complex with Apaf-1 and dATP. Apoptosome causes serial activation of caspases-9, -3 and -7 to initiate cell death. In cancers, miR-184 exhibits dual effects on apoptosis. It acts as an inhibitor of apoptosis by downregulating caspase-3, and caspase-6, in hepatocellular carcinoma. Conversely, in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, miR-184 induces apoptosis by inhibiting anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 and increasing caspase-3 and caspace 9. TNF tumor necrosis factor, FasL Fas ligand, TRAIL TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand, FADD Fas-associated death domain, DISC Death-inducing signaling complex, Bid BH3-interacting domain death agonist, Bcl-2 B-cell lymphoma 2, Apaf-1 Apoptotic protease-activating factor 1, dATP Deoxyadenosine triphosphate, TRAIL-R TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor 1, XIAP X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis.
