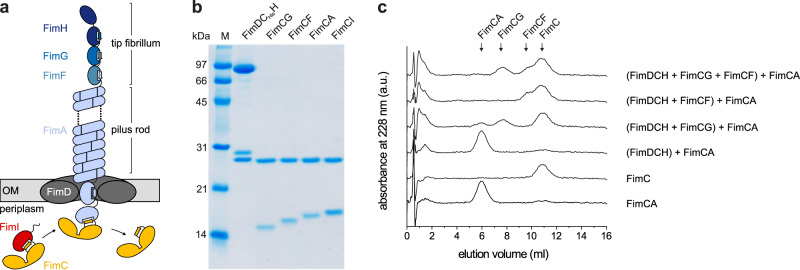
Fig. 1. In vitro reconstitution of type 1 pilus rod assembly.
a Architecture and subunit composition of the type 1 pilus. The linear tip fibrillum consists of the adhesin FimH and the minor subunits FimG and FimF. It is attached to the helical pilus rod that may consist of several thousand copies of the main subunit FimA2,9,11. Pilus assembly is catalyzed by the assembly platform FimD in the outer membrane (OM)20. Only subunits bound to the periplasmic chaperone FimC are assembly-competent and recognized by FimD27,28. The mechanism of incorporation of the assembly terminator subunit FimI (red) is the focus of this study. b Coomassie-stained polyacrylamide-SDS gel of the purified type 1 pilus subcomplexes (25 pmol each) used in this study. A representative result of three independent repetitions is shown. c Analytical cation ion exchange chromatography runs, monitoring the decrease in the concentrations of free FimCA complexes during FimD-catalyzed pilus rod assembly in vitro. FimDCH (0.35 µM) was preincubated with or without an 8-fold molar excess of FimCG or FimCF or both for 5 min at 37 °C. After addition of FimCA (final concentrations of FimDCH and FimCA were 0.25 and 5 µM, respectively) and incubation for 10 min at 37 °C, the reactions were stopped by rapid cooling on ice. The remaining, free FimC-subunit complexes were separated and quantified by cation exchange chromatography at 4 °C and pH 6.7. Reference elution profiles for 5 µM FimC and 5 µM FimCA are shown at the bottom of the panel. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.