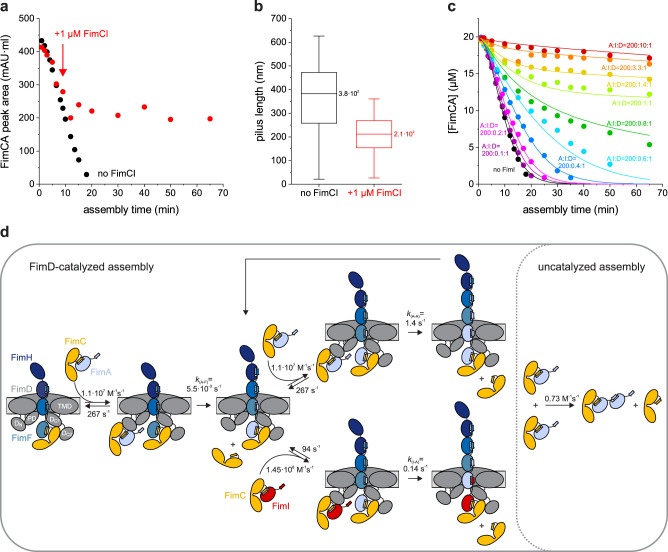
Fig. 2. FimI inhibits type 1 pilus rod assembly.
a Kinetics of FimD-catalyzed FimA assembly at pH 8.0 and 23 °C, recorded in absence of FimCI (black) or with FimCI added to 1 μM after nine minutes of the reaction (red). The time point of FimCI addition is indicated by an arrow. FimDCH (0.35 µM) was preincubated with an 8-fold molar excess of FimCG and FimCF for 30 min at 23 °C. After addition of FimCA (final concentrations of FimDCH and FimCA were 0.1 and 20 µM) and further incubation at 23 °C for defined periods of time, the reaction mixtures were analyzed by analytical cation exchange chromatography at 4 °C and pH 6.0. FimA assembly was monitored by recording the decrease in FimCA peak area with time. b Box plots of pilus length distributions of the two reactions shown in panel (a). Samples taken after 65 min of assembly were analyzed by negative-stain electron microscopy and the length of 200 pili each was measured. The box encloses the second and third quartile, the horizontal line indicates the median and the whiskers the smallest and largest value of the distribution (n = 200). c Kinetics of FimD-catalyzed FimA assembly in presence of different FimCI concentrations at pH 8.0 and 23 °C. Molar ratios between FimCA, FimCI and FimD (A:I:D) are indicated. Initial concentrations were 0.1 µM FimD, 20 µM FimCA and 0.01–1 µM FimCI. Solid lines show the result of a global fit of the data according to the model depicted in (d). d Minimal mechanism for type 1 pilus rod assembly and assembly inhibition in vitro. The rate constants for binding/dissociation of FimCA and FimCI to/from FimDN and for uncatalyzed FimA assembly were kept fixed during fitting. Rate constants for FimCA had been measured previously51. The domains of FimD are denoted: N-terminal (DN), plug (PD), transmembrane (TMD) and C-terminal domains (DC1, DC2). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.