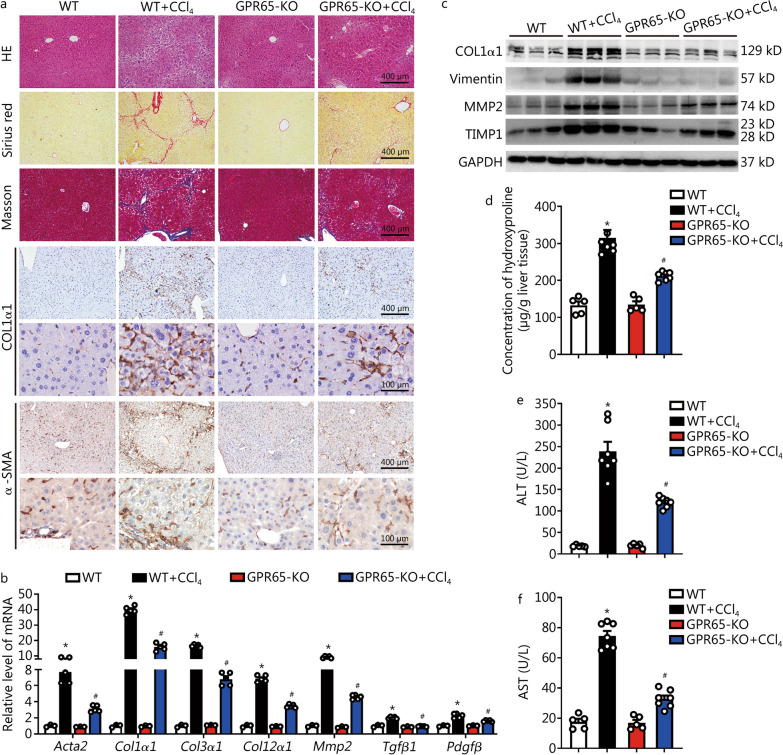
Fig. 3.
Gpr65 deficiency alleviates hepatic fibrosis induced by CCl4. a WT and GPR65-KO mice were divided into 4 groups: WT, WT + CCl4, GPR65-KO and GPR65-KO + CCl4. Hepatic fibrosis was evaluated by HE staining, Sirius red staining, Masson’s trichrome staining and IHC for COL1α1 and α-SMA. Scale bar = 100 μm for 40 × and 400 μm for 10 × . b qRT-PCR was used to assess the mRNA level of Acta2, Col1α1, Col3α1, Col12α1, Mmp2, Tgfβ1 and Pdgfβ (n = 3, 5, 3, 5). c Western blotting was used to determine the protein level of COL1α1, vimentin, MMP2 and TIMP1. d The content of hepatic hydroxyproline was quantified in livers of each group (n = 5, 7, 5, 7). Serum ALT (e) and AST (f) level were examined (n = 5, 7, 5, 7). *P < 0.05 vs. WT; #P < 0.05 vs. WT + CCl4. CCl4 carbon tetrachloride, IHC immunohistochemistry, KO knockout, qRT-PCR quantitative real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction, COL1α1 collagen type I alpha 1, α-SMA α-smooth muscle actin, MMP2 matrix metalloproteinase 2, TIMP1 tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1, ALT alanine aminotransferase, AST aspartate aminotransferase