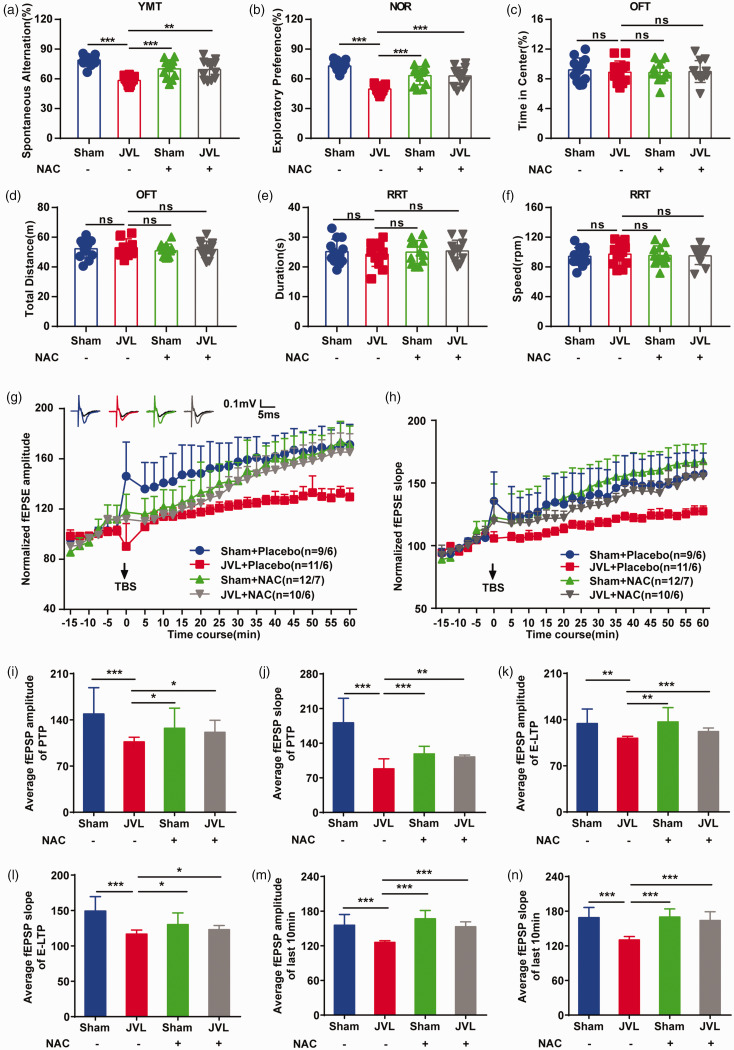
Figure 4.
NAC supplementation rescued impaired learning and memory ability and damaged hippocampal LTP in cerebral venous congestion rats. (a) Spontaneous alternation in the Y-maze (n = 12). (b) Exploratory preference in the NOR (n = 12). (c, d) Continued.Percentage of time spent in the center area and total distance in the center area in the OFT (n = 12). (e, f) Duration and speed to fall in the RRT (n = 12). (g, h) Summary plots of normalized fEPSP amplitude (%) and slope (%) during the recording period in the dentate gyrus. The fEPSP was induced by 5 × TBS (arrow). Inset traces: representative traces of fEPSP before (black curve) and after (blue curve for Sham + Placebo; red curve for JVL + Placebo; green curve for Sham + NAC; grey curve for JVL + NAC) the induction of potentiation. (i–n) Normalized fEPSP amplitude and slope for the PTP (0–2 min post-TBS) (i, j), E-LTP (15–20 min post-TBS) (k, l), and last 10 min (m, n). All data are presented as the mean ± SD. Statistical significance was calculated using a two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test (a–f, i–n) or repeated-measures analysis of variance (g, h). Dots depict individual samples in a–f. Data are representative of at least five independent experiments. ns, with no significance; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. NOR: novel object recognition; OFT: open-field test; RRT: rotarod test; LTP: long-term potentiation; fEPSP: field excitatory postsynaptic potential; TBS: theta-burst stimulation; PTP: post-tetanic potentiation; E-LTP: early-LTP; NAC: N-acetyl-L-cysteine.