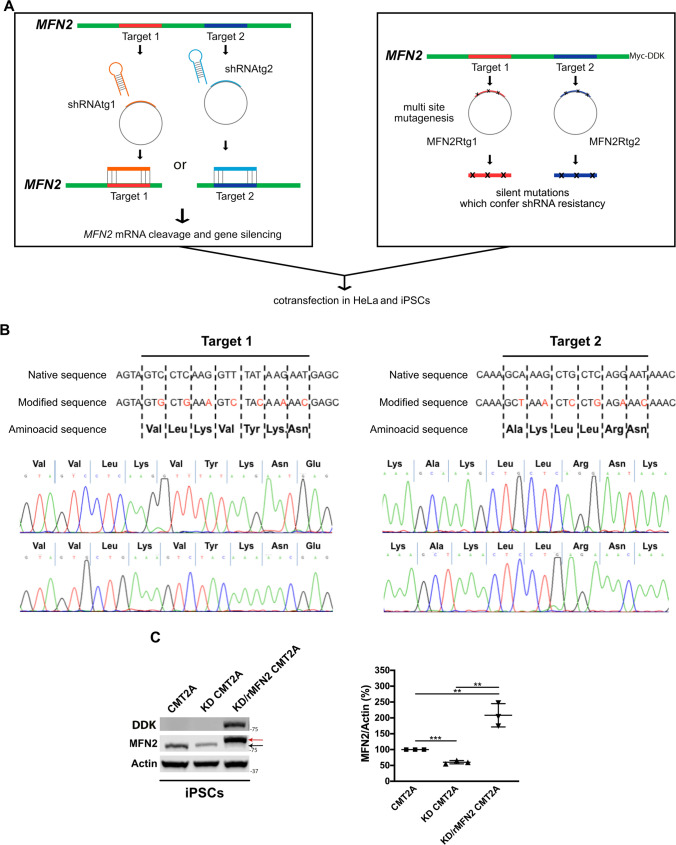
Fig. 1.
CMT2A iPSCs showed silencing of endogenous MFN2 and overexpression of modified exogenous MFN2 after combined RNAi/gene therapy. A Schematic representation of MFN2 gene silencing and MFN2 multi-site mutagenesis experiments in CMT2A iPSCs and HeLa cells. B Diagram of multi-site mutagenesis performed on target1 and target2 of human MFN2, respectively. Mutated nucleotides are in red. There was no change in the amino acid sequences between native and mutated sequences. Direct sequencing of vector-mutated sequences confirmed the presence of inserted mutations. C Representative Western blot of endogenous MFN2 (endoMFN2, black arrow) and RNAi-resistant exogenous WT Myc-DDK MFN2 (exoMFN2, red arrow) in CMT2A iPSCs (CMT2A) after shRNAtg2 transduction (KD-CMT2A) or after shRNAtg2 and MFN2Rtg2 co-transduction (KD/rMFN2-CMT2A). The specific expression of exogenous MFN2 (Myc-DDK MFN2) was also confirmed by Western blot using an antibody for DYKDDDDK Tag (DDK). Densitometric quantification (n = 3). Error bars indicate SEM of MFN2/Actin expression. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, Student’s t-test