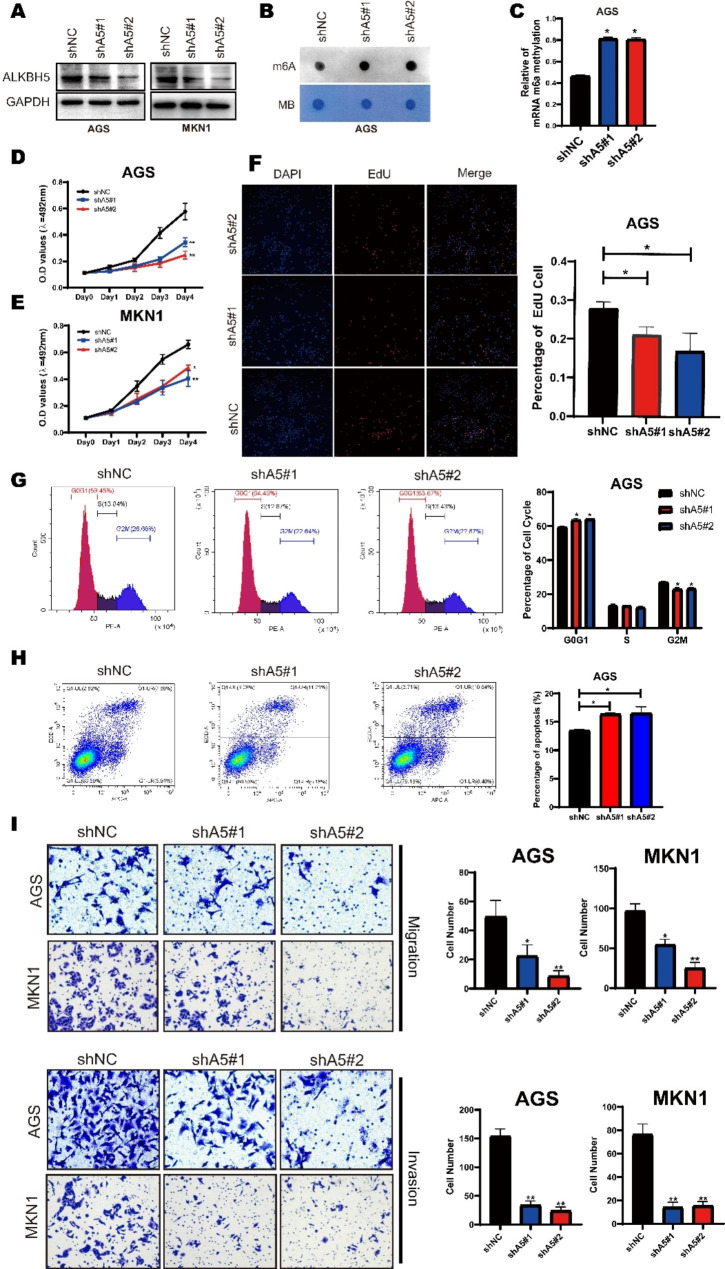
Fig. 2.
ALKBH5 affects gastric cancer cell progression in multiple ways. (A) Western blotting of ALKBH5 protein levels in MKN1 (right) and AGS (left) cells after ALKBH5 knockdown. (B) mRNA isolated from GC cells with knockdown of ALKBH5 was analyzed by spot hybridization with m6A antibody. MB (methylene blue) staining was used as a control. (C) Through EpiQuik M6A RNA Methylation Quantification Kit colorimetric method to detect the m6a level from the model. (D-E) MTT Cell Proliferation and Cytotoxicity Assay Kit for two ALKBH5 knockdown sequences and control in AGS and MKN1 cells. (F) ALKBH5 knockdown and control AGS cells were stained with azide 594 (red) to detect EdU and DAPI (blue) to stain cell nuclei. Fluorescence images were obtained and analyzed by fluorescence microscopy (left). Values are expressed as mean ± SD compared to the control group, n = 3 * p < 0.05 (right). (G) Cell cycle analysis using propidium iodide (PI) staining of ALKBH5 knockdown and control AGS cells. (left): Representative images. (right): Quantitative data. (H) ALKBH5 knockdown and apoptosis analysis using membrane coupling protein V/propidium iodide (PI) staining in control AGS cells. (left): Representative images. (right): Quantitative data. (I) Transwell cell migration (upper) analysis of ALKBH5 knockdown and control groups in AGS and MKN1 cells. Matrigel matrix gel invasion assay (bottom) of ALKBH5 knockdown and control groups in AGS and MKN1 cells. Left: Representative images. Right: quantitative data. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 and ∗∗∗ p < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA; t-test). shA5-1, shALKBH5-1; sh A5-2, sh ALKBH5-2; shNC, negative control shRNA. all in vitro assays were repeated biologically 3 times